A Sensitive and Simple HPLC-UV Method for Trace Level Quantification of Ethyl p-Toluenesulfonate and Methyl p-Toluenesulfonate, Two Potential Genotoxins in Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
- PMID: 22145110
- PMCID: PMC3221504
- DOI: 10.3797/scipharm.1106-23
A Sensitive and Simple HPLC-UV Method for Trace Level Quantification of Ethyl p-Toluenesulfonate and Methyl p-Toluenesulfonate, Two Potential Genotoxins in Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
Abstract
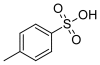
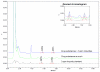
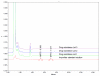
A sensitive and simple HPLC/UV method has been developed and validated for the determination of two potential genotoxic impurities, namely methyl p-toluenesulfonate (MPTS) and ethyl p-toluenesulfonate (EPTS) at trace levels in Pemetrexed sodium API. Applying the concept of threshold of toxicological concern (TTC), a limit of 3 ppm each for both genotoxins was calculated based on the maximum daily dose of API. A reversed phase LC method using UV detection was developed and validated. The method was found to be specific and selective for the application. The limit of detection (LOD) and limit of quantitation (LOQ) for both MPTS and EPTS was found to be 0.15 ppm (0.009 μg mL(-1)) and 0.5 ppm (0.03 μg mL(-1)), respectively, with respect to sample concentration. The calibration curves of MPTS and EPTS were linear over the concentration range from LOQ to 6 μg/mL. The method was found to be specific, precise, linear and accurate and has been successfully applied to determine the two genotoxins in commercial batches of the API.
Keywords: Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient; Daily dosage; Genotoxin; Threshold of toxicological concern; Validation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Low level determinations of methyl methanesulfonate and ethyl methanesulfonate impurities in emtricitabine active pharmaceutical ingredient by LC/MS/MS using electrospray ionization.Anal Chem Insights. 2011;6:21-8. doi: 10.4137/ACI.S6471. Epub 2011 Mar 10. Anal Chem Insights. 2011. PMID: 21760706 Free PMC article.
-
Development of chromatographic methods for the determination of genotoxic impurities in cloperastine fendizoate.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2012 Mar 5;61:230-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2011.12.014. Epub 2011 Dec 19. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2012. PMID: 22226040
-
Application of analytical quality by design principles for the determination of alkyl p-toluenesulfonates impurities in Aprepitant by HPLC. Validation using total-error concept.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018 Feb 20;150:152-161. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2017.12.009. Epub 2017 Dec 7. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018. PMID: 29245084
-
Low level determinations of methyl methanesulfonate and ethyl methanesulfonate impurities in Lopinavir and Ritonavir Active pharmaceutical ingredients by LC/MS/MS using electrospray ionization.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2011 May 15;55(2):379-84. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2011.01.039. Epub 2011 Feb 24. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2011. PMID: 21353429
-
Utilization of Photochemically Induced Fluorescence Detection for HPLC Determination of Genotoxic Impurities in the Vortioxetine Manufacturing Process.J Chromatogr Sci. 2016 Oct 17;54(9):1625-1630. doi: 10.1093/chromsci/bmw116. J Chromatogr Sci. 2016. PMID: 27368342
References
-
- Griesser H, Öhrlein R, Schwab W, Ehrler R, Jäger V. 3-Nitropropanal, 3-Nitropropanol, and 3-Nitropropanal Dimethyl Acetal. Org Synth. 2004;10:577.
-
- Furuta K, Gao QZ, Yamamoto H. Chiral (Acyloxy)borane Complex-catalyzed Asymmetric Diels-Alder Reaction:(1R)-1,3,4-Trimethyl-3-cyclohexene-1-carboxaldehyde. Org Synth. 1998;9:722.
-
- Imwinkelried R, Schiess M, Seebach D. Diisopropyl (2S,3S)-2,3-O-isopropylidenetartrate. Org Synth. 1993;8:201.
-
- Müller L, Mauthe RJ, Riley CM, Andino MM, Antonis DD, Beels C, DeGeorge J, De Knaep AG, Ellison D, Fagerland JA, Frank R, Fritschel B, Galloway S, Harpur E, Humfrey CD, Jacks AS, Jagota N, Mackinnon J, Mohan G, Ness DK, O’Donovan MR, Smith MD, Vudathala G, Yotti L. A rationale for determining, testing, and controlling specific impurities in pharmaceuticals that possess potential for genotoxicity. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2006;44:198–211. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.yrtph.2005.12.001. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dobo KL, Greene N, Cyr MO, Caron S, Ku WW. The application of structure-based assessment to support safety and chemistry diligence to manage genotoxic impurities in active pharmaceutical ingredients during drug development. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2006;44:282–93. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.yrtph.2006.01.004. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
