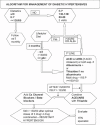
Management of diabetic hypertensives
- PMID: 22145142
- PMCID: PMC3230084
- DOI: 10.4103/2230-8210.86982
Management of diabetic hypertensives
Abstract
Hypertension occurs twice as commonly in diabetics than in comparable nondiabetics. Patients with both disorders have a markedly higher risk for premature microvascular and macrovascular complications. Aggressive control of blood pressure (BP) reduces both micro- and macrovascular complications. In diabetic hypertensives, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs) are the first line in management of hypertension, and can be replaced by angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) if patients are intolerant of them. Recent studies suggest ARBs to be on par with ACEI in reducing both macro- and microvascular risks. Adding both these agents may have a beneficial effect on proteinuria, but no extra macrovascular risk reduction. Thiazides can also be used as first line drugs, but are better used along with ACEI/ARBs. Beta-blockers [especially if the patient has coronary artery disease] and calcium channel blockers are used as second line add-on drugs. Multidrug regimens are commonly needed in diabetic hypertensives. Achieving the target BP of <130/80 is the priority rather than the drug combination used in order to arrest and prevent the progression of macro- and microvascular complications in diabetic hypertensives.
Keywords: Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor; angiotensin II receptor blockers; diabetes mellitus; hypertension; life-style modification.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Paul B, Sapra B, Maheswari S, Goyal RK. Role of losartan therapy in the management of diabetic hypertension. J Assoc Physicians India. 2000;48:514–7. - PubMed
-
- Sowers JR, Haffner S. Treatment of CV and renal risk factors in the diabetic hypertensive. Hypertension. 2002;40:781–8. - PubMed
-
- Tarnow L, Rossing P, Gall MA, Nielsen FS, Parving HH. Prevalence of arterial hypertension in diabetic patients before and after the JNC-V. Diabetes Care. 1994;17:1247–51. - PubMed
-
- Sowers JR, Haffner S. Treatment of cardiovascular and renal risk factors in the diabetic hypertensive. Hypertension. 2002;40:781–8. - PubMed
-
- Gress TW, Nieto FJ, Shahar E, Wofford MR, Brancati FL. Hypertension and antihypertensive therapy as risk factors for type 2 diabetes mellitus.Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:905–12. - PubMed