Effects of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG supplementation on cow's milk allergy in a mouse model
- PMID: 22145744
- PMCID: PMC3261804
- DOI: 10.1186/1710-1492-7-20
Effects of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG supplementation on cow's milk allergy in a mouse model
Abstract
Background: Cow's milk allergy (CMA) is one of the most prevalent human food-borne allergies, particularly in infants and young children from developed countries. Our study aims to evaluate the effects of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG) administration on CMA development using whole cow's milk proteins (CMP) sensitized Balb/C mice by two different sensitization methods.
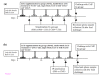
Methods: LGG supplemented mice were either sensitized orally with CMP and cholera toxin B-subunit (CTB) as adjuvant, or intraperitoneally (IP) with CMP but without the adjuvant. Mice were then orally challenged with CMP and allergic responses were accessed by monitoring hypersensitivity scores, measuring the levels of CMP-specific immunoglobulins (IgG1, IgG2a and IgG) and total IgE from sera, and cytokines (IL-4 and IFN-γ) from spleen lysates.
Results: Sensitization to CMP was successful only in IP sensitized mice, but not in orally sensitized mice with CMP and CTB. Interestingly, LGG supplementation appeared to have reduced cow's milk allergy (CMA) in the IP group of mice, as indicated by lowered allergic responses.
Conclusions: Adjuvant-free IP sensitization with CMP was successful in inducing CMA in the Balb/C mice model. LGG supplementation favourably modulated immune reactions by shifting Th2-dominated trends toward Th1-dominated responses in CMP sensitized mice. Our results also suggest that oral sensitization by the co-administration of CMP and CTB, as adjuvant, might not be appropriate to induce CMA in mice.
Figures

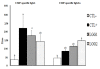

Similar articles
-
Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG for Cow's Milk Allergy in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Pediatr. 2021 Oct 22;9:727127. doi: 10.3389/fped.2021.727127. eCollection 2021. Front Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34746056 Free PMC article.
-
Administration of Extensive Hydrolysates From Caseins and Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG Probiotic Does Not Prevent Cow's Milk Proteins Allergy in a Mouse Model.Front Immunol. 2020 Sep 11;11:1700. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01700. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33042105 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo evidence of cross-reactivity between cow's milk and soybean proteins in a mouse model of food allergy.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2012;158(4):335-46. doi: 10.1159/000333562. Epub 2012 Apr 3. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22472742
-
Extensively hydrolyzed casein formula alone or with L. rhamnosus GG reduces β-lactoglobulin sensitization in mice.Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2017 May;28(3):230-237. doi: 10.1111/pai.12687. Epub 2017 Jan 24. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2017. PMID: 27992668
-
Cow's milk protein allergy and intolerance in infancy. Some clinical, epidemiological and immunological aspects.Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 1994;5(5 Suppl):1-36. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 1994. PMID: 7704117 Review.
Cited by
-
Use of animal models to investigate major allergens associated with food allergy.J Allergy (Cairo). 2013;2013:635695. doi: 10.1155/2013/635695. Epub 2013 Apr 11. J Allergy (Cairo). 2013. PMID: 23690797 Free PMC article.
-
Microbiota and Food Allergy.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2019 Aug;57(1):83-97. doi: 10.1007/s12016-018-8723-y. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30564985 Review.
-
Research progress on the mechanism of probiotics regulating cow milk allergy in early childhood and its application in hypoallergenic infant formula.Front Nutr. 2024 Feb 14;11:1254979. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1254979. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38419849 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG for Cow's Milk Allergy in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Pediatr. 2021 Oct 22;9:727127. doi: 10.3389/fped.2021.727127. eCollection 2021. Front Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34746056 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative PCR Assays for the Strain-Specific Identification and Enumeration of Probiotic Strain Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus X253.Foods. 2022 Jul 30;11(15):2282. doi: 10.3390/foods11152282. Foods. 2022. PMID: 35954048 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

