CXCR7 antagonism prevents axonal injury during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis as revealed by in vivo axial diffusivity
- PMID: 22145790
- PMCID: PMC3305694
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-2094-8-170
CXCR7 antagonism prevents axonal injury during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis as revealed by in vivo axial diffusivity
Abstract
Background: Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is characterized by the pathological trafficking of leukocytes into the central nervous system (CNS). Using the murine MS model, experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), we previously demonstrated that antagonism of the chemokine receptor CXCR7 blocks endothelial cell sequestration of CXCL12, thereby enhancing the abluminal localization of CXCR4-expressing leukocytes. CXCR7 antagonism led to decreased parenchymal entry of leukocytes and amelioration of ongoing disease during EAE. Of note, animals that received high doses of CXCR7 antagonist recovered to baseline function, as assessed by standard clinical scoring. Because functional recovery reflects axonal integrity, we utilized diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) to evaluate axonal injury in CXCR7 antagonist- versus vehicle-treated mice after recovery from EAE.
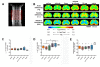
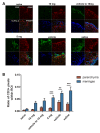
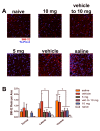
Methods: C57BL6/J mice underwent adoptive transfer of MOG-reactive Th1 cells and were treated daily with either CXCR7 antagonist or vehicle for 28 days; and then evaluated by DTI to assess for axonal injury. After imaging, spinal cords underwent histological analysis of myelin and oligodendrocytes via staining with luxol fast blue (LFB), and immunofluorescence for myelin basic protein (MBP) and glutathione S-transferase-π (GST-π). Detection of non-phosphorylated neurofilament H (NH-F) was also performed to detect injured axons. Statistical analysis for EAE scores, DTI parameters and non-phosphorylated NH-F immunofluorescence were done by ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-hoc test. For all statistical analysis a p < 0.05 was considered significant.
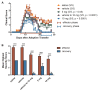
Results: In vivo DTI maps of spinal cord ventrolateral white matter (VLWM) axial diffusivities of naïve and CXCR7 antagonist-treated mice were indistinguishable, while vehicle-treated animals exhibited decreased axial diffusivities. Quantitative differences in injured axons, as assessed via detection of non-phosphorylated NH-F, were consistent with axial diffusivity measurements. Overall, qualitative myelin content and presence of oligodendrocytes were similar in all treatment groups, as expected by their radial diffusivity values. Quantitative assessment of persistent inflammatory infiltrates revealed significant decreases within the parenchyma of CXCR7 antagonist-treated mice versus controls.
Conclusions: These data suggest that CXCR7 antagonism not only prevents persistent inflammation but also preserves axonal integrity. Thus, targeting CXCR7 modifies both disease severity and recovery during EAE, suggesting a role for this molecule in both phases of disease.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Axial diffusivity is the primary correlate of axonal injury in the experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis spinal cord: a quantitative pixelwise analysis.J Neurosci. 2009 Mar 4;29(9):2805-13. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4605-08.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19261876 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring experimental autoimmune optic neuritis using multimodal imaging.Neuroimage. 2018 Jul 15;175:327-339. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2018.04.004. Epub 2018 Apr 6. Neuroimage. 2018. PMID: 29627590
-
Diffusion tensor imaging detects treatment effects of FTY720 in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis mice.NMR Biomed. 2013 Dec;26(12):1742-50. doi: 10.1002/nbm.3012. Epub 2013 Aug 13. NMR Biomed. 2013. PMID: 23939596 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of cannabinoid receptor activation as a neuroprotective strategy for EAE and stroke.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2009 Jun;4(2):249-59. doi: 10.1007/s11481-009-9148-4. Epub 2009 Mar 3. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19255856 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment-resistant inflammatory demyelinating pseudotumor with Marburg-like features: A narrative review-based treatment approach.J Res Med Sci. 2025 Feb 28;30:9. doi: 10.4103/jrms.jrms_477_24. eCollection 2025. J Res Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40200967 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Disruption of placental ACKR3 impairs growth and hematopoietic development of offspring.Development. 2024 Feb 15;151(4):dev202333. doi: 10.1242/dev.202333. Epub 2024 Feb 23. Development. 2024. PMID: 38300826 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting IFN-λ Signaling Promotes Recovery from Central Nervous System Autoimmunity.J Immunol. 2022 Mar 15;208(6):1341-1351. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2101041. Epub 2022 Feb 18. J Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35181638 Free PMC article.
-
CXCR7 Targeting and Its Major Disease Relevance.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Jun 21;9:641. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00641. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29977203 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of astroglial NF-κB enhances oligodendrogenesis following spinal cord injury.J Neuroinflammation. 2013 Jul 23;10:92. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-10-92. J Neuroinflammation. 2013. PMID: 23880092 Free PMC article.
-
DGAT1 inhibits retinol-dependent regulatory T cell formation and mediates autoimmune encephalomyelitis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Feb 19;116(8):3126-3135. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1817669116. Epub 2019 Feb 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 30718413 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Forte M, Gold BG, Marracci G, Chaudhary P, Basso E, Johnsen D, Yu X, Fowlkes J, Rahder M, Stem K, Bernardi P, Bourdette D. Cyclophilin D inactivation protects axons in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, an animal model of multiple sclerosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104(18):7558–63. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0702228104. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

