The prefrontal cortex and hybrid learning during iterative competitive games
- PMID: 22145879
- PMCID: PMC3302724
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2011.06223.x
The prefrontal cortex and hybrid learning during iterative competitive games
Abstract
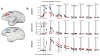
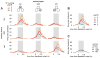
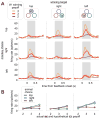
Behavioral changes driven by reinforcement and punishment are referred to as simple or model-free reinforcement learning. Animals can also change their behaviors by observing events that are neither appetitive nor aversive when these events provide new information about payoffs available from alternative actions. This is an example of model-based reinforcement learning and can be accomplished by incorporating hypothetical reward signals into the value functions for specific actions. Recent neuroimaging and single-neuron recording studies showed that the prefrontal cortex and the striatum are involved not only in reinforcement and punishment, but also in model-based reinforcement learning. We found evidence for both types of learning, and hence hybrid learning, in monkeys during simulated competitive games. In addition, in both the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and orbitofrontal cortex, individual neurons heterogeneously encoded signals related to actual and hypothetical outcomes from specific actions, suggesting that both areas might contribute to hybrid learning.
© 2011 New York Academy of Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Sutton RS, Barto AG. Reinforcement learning: an introduction. MIT Press; Massachusetts: 1998.
-
- Tolman EC. Cognitive maps in rats and men. Psychol Rev. 1948;55:189–208. - PubMed
-
- Balleine BW, Dickinson A. Goal-directed instrumental action: contingency and incentive learning and their cortical substrates. Neuropharmacology. 1998;37:407–419. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

