The proline TP53 variant stimulates likely lymphangiogenesis in an orthotopic mouse model of pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 22146521
- PMCID: PMC3261666
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2011.521
The proline TP53 variant stimulates likely lymphangiogenesis in an orthotopic mouse model of pancreatic cancer
Abstract
Background: Pancreatic cancer is a deadly disease characterised by high incidence of TP53 mutations. Restoration of TP53 function is perceived as a highly attractive therapeutic strategy, whose effects are not well characterised.
Methods: The current work adapted an inducible strategy of stage-specific reexpression of wild-type (wt) TP53 in an in vivo orthotopic mouse model of pancreatic cancer.
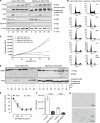
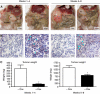
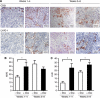
Results: The reconstitution of wt TP53 function in TP53-mutant DanG and MiaPaCa-2 cells caused G1 cell cycle arrest but no evidence of apoptosis induction. Consistent with subcutaneous xenograft models, we found that wt TP53 reduced primary tumour growth. Wt TP53 reexpression during early tumour growth led to significant increase in vascularisation. This correlated with an unexpectedly high rate of micro-metastases in lymph nodes of animals with wt TP53 induction, despite the 90% decrease in median primary tumour weight. Reexpression of wt TP53 later in tumour development did not significantly affect the number of CD31-reactive vessels, but increased lymphatic vessel density.
Conclusion: The increased number of lymphatic vessels and micro-metastases suggests that wt TP53 induction complexly affected the biology of different tumour constituents of pancreatic cancer. Our observation suggests that combination of the inducible system with an orthotopic model can yield important insights into in vivo pancreatic cancer biology.
Figures

References
-
- Alves F, Contag S, Missbach M, Kaspareit J, Nebendahl K, Borchers U, Heidrich B, Streich R, Hiddemann W (2001) An orthotopic model of ductal adenocarcinoma of the pancreas in severe combined immunodeficient mice representing all steps of the metastatic cascade. Pancreas 23: 227–235 - PubMed
-
- American Cancer Society (2007) Cancer Facts & Figures 2007. American Cancer Society: Atlanta, GA, pp 1–52
-
- Bardeesy N, DePinho RA (2002) Pancreatic cancer biology and genetics. Nat Rev Cancer 2: 897–909 - PubMed
-
- Blouw B, Song H, Tihan T, Bosze J, Ferrara N, Gerber HP, Johnson RS, Bergers G (2003) The hypoxic response of tumors is dependent on their microenvironment. Cancer Cell 4: 133–146 - PubMed
-
- Braithwaite AW, Prives CL (2006) p53: more research and more questions. Cell Death Differ 13: 877–880 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

