A2A and A3 adenosine receptor expression in rheumatoid arthritis: upregulation, inverse correlation with disease activity score and suppression of inflammatory cytokine and metalloproteinase release
- PMID: 22146575
- PMCID: PMC3334647
- DOI: 10.1186/ar3527
A2A and A3 adenosine receptor expression in rheumatoid arthritis: upregulation, inverse correlation with disease activity score and suppression of inflammatory cytokine and metalloproteinase release
Abstract
Introduction: The reduction of the inflammatory status represents one of the most important targets in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). A central role of A2A and A3 adenosine receptors (ARs) in mechanisms of inflammation has been reported in different pathologies. The primary aim of this study was to investigate the A2A and A3ARs and their involvement in RA progression measured by Disease Activity Score in 28 or 44 joints (DAS28 or DAS).
Methods: ARs were analyzed by saturation binding assays, mRNA and Western blotting analysis in lymphocytes from early and established RA patients. The effect of A2A and A3AR agonists in nuclear factor kB (NF-kB) pathway was evaluated. Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) release was carried out by A2A and A3AR activation. AR pharmacological regulation in matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MMP-1) and metalloproteinase-3 (MMP-3) release was also studied.
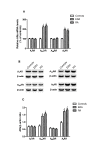
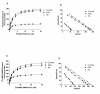
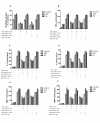
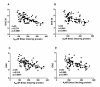
Results: In lymphocytes obtained from RA patients, A2A and A3ARs were up-regulated if compared with healthy controls. A2A and A3AR activation inhibited the NF-kB pathway and diminished inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6. A2A and A3AR agonists mediated a reduction of MMP-1 and MMP-3 release. A2A and A3AR density inversely correlated with DAS28 and DAS suggesting a direct role of the endogenous activation of these receptors in the control of RA joint inflammation.
Conclusions: Taken together these data demonstrate that the inflammatory and clinical responses in RA are regulated by A2A and A3ARs and support the use of A2A and/or A3AR agonists as novel and effective pharmacological treatment in RA patients.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role and Function of A2A and A₃ Adenosine Receptors in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis, Psoriatic Arthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Mar 24;18(4):697. doi: 10.3390/ijms18040697. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28338619 Free PMC article.
-
Pulsed electromagnetic fields increased the anti-inflammatory effect of A₂A and A₃ adenosine receptors in human T/C-28a2 chondrocytes and hFOB 1.19 osteoblasts.PLoS One. 2013 May 31;8(5):e65561. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065561. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23741498 Free PMC article.
-
Normalization of A2A and A3 adenosine receptor up-regulation in rheumatoid arthritis patients by treatment with anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha but not methotrexate.Arthritis Rheum. 2009 Oct;60(10):2880-91. doi: 10.1002/art.24794. Arthritis Rheum. 2009. PMID: 19790066
-
Perspective and Potential of A2A and A3 Adenosine Receptors as Therapeutic Targets for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis.Curr Pharm Des. 2019;25(26):2859-2874. doi: 10.2174/1381612825666190710111658. Curr Pharm Des. 2019. PMID: 31291875 Review.
-
The A3 adenosine receptor (A3AR): therapeutic target and predictive biological marker in rheumatoid arthritis.Clin Rheumatol. 2016 Sep;35(9):2359-62. doi: 10.1007/s10067-016-3202-4. Epub 2016 Feb 17. Clin Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 26886128 Review.
Cited by
-
Adenosine signaling during acute and chronic disease states.J Mol Med (Berl). 2013 Feb;91(2):173-81. doi: 10.1007/s00109-013-0997-1. Epub 2013 Jan 23. J Mol Med (Berl). 2013. PMID: 23340998 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multi-omic landscape of rheumatoid arthritis: re-evaluation of drug adverse effects.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2014 Nov 4;2:59. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2014.00059. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2014. PMID: 25414848 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-206 is involved in the pathogenesis of ulcerative colitis via regulation of adenosine A3 receptor.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 3;8(1):705-721. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13525. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27893428 Free PMC article.
-
The Purinergic System as a Pharmacological Target for the Treatment of Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases.Pharmacol Rev. 2019 Jul;71(3):345-382. doi: 10.1124/pr.117.014878. Pharmacol Rev. 2019. PMID: 31235653 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adenosine-Induced NLRP11 in B Lymphoblasts Suppresses Human CD4+ T Helper Cell Responses.J Immunol Res. 2020 Aug 3;2020:1421795. doi: 10.1155/2020/1421795. eCollection 2020. J Immunol Res. 2020. PMID: 32832566 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Weissmann G. The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 2006;64:12–15. - PubMed
-
- Belavic JM. Annual Drug Update 2010 in review. Nurse Pract. 2011;36:10–22. - PubMed
-
- Furst DE, Keystone EC, Fleischmann R, Breedveld FC, Burmester GR, De Benedetti F, Dörner T, Emery P, Fleischmann R, Gibofsky A, Kalden JR, Kavanaugh A, Kirkham B, Mease P, Sieper J, Singer NG, Smolen JS, Van Riel PL, Weisman MH, Winthrop K. Updated consensus statement on biological agents for the treatment of rheumatic diseases. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69:2–29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

