Population divergence with or without admixture: selecting models using an ABC approach
- PMID: 22146980
- PMCID: PMC3330690
- DOI: 10.1038/hdy.2011.116
Population divergence with or without admixture: selecting models using an ABC approach
Abstract
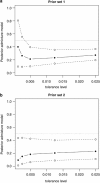
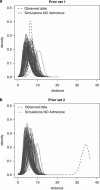
Genetic data have been widely used to reconstruct the demographic history of populations, including the estimation of migration rates, divergence times and relative admixture contribution from different populations. Recently, increasing interest has been given to the ability of genetic data to distinguish alternative models. One of the issues that has plagued this kind of inference is that ancestral shared polymorphism is often difficult to separate from admixture or gene flow. Here, we applied an approximate Bayesian computation (ABC) approach to select the model that best fits microsatellite data among alternative splitting and admixture models. We performed a simulation study and showed that with reasonably large data sets (20 loci) it is possible to identify with a high level of accuracy the model that generated the data. This suggests that it is possible to distinguish genetic patterns due to past admixture events from those due to shared polymorphism (population split without admixture). We then apply this approach to microsatellite data from an endangered and endemic Iberian freshwater fish species, in which a clustering analysis suggested that one of the populations could be admixed. In contrast, our results suggest that the observed genetic patterns are better explained by a population split model without admixture.
Figures
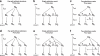



References
-
- Alves MJ, Coelho MM. Genetic variation and population subdivision of the endangered Iberian cyprinid Chondrostoma lusitanicum. J Fish Biol. 1994;44:627–636.
-
- Beaumont M. Approximate Bayesian computation in evolution and ecology. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst. 2010;41:379–406.
-
- Beaumont MA.2008. Joint determination of tree topology and population history. In: Matsumura S, Forster P, Renfrew C (eds) Simulation, Genetics, and Human Prehistory. McDonald Institute for Archaeological Research: Cambridge; 135–154.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

