Disclosing pathogenic genetic variants to research participants: quantifying an emerging ethical responsibility
- PMID: 22147367
- PMCID: PMC3290777
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.127845.111
Disclosing pathogenic genetic variants to research participants: quantifying an emerging ethical responsibility
Abstract
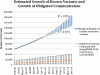
There is an emerging consensus that when investigators obtain genomic data from research participants, they may incur an ethical responsibility to inform at-risk individuals about clinically significant variants discovered during the course of their research. With whole-exome sequencing becoming commonplace and the falling costs of full-genome sequencing, there will be an increasingly large number of variants identified in research participants that may be of sufficient clinical relevance to share. An explicit approach to triaging and communicating these results has yet to be developed, and even the magnitude of the task is uncertain. To develop an estimate of the number of variants that might qualify for disclosure, we apply recently published recommendations for the return of results to a defined and representative set of variants and then extrapolate these estimates to genome scale. We find that the total number of variants meeting the threshold for recommended disclosure ranges from 3955-12,579 (3.79%-12.06%, 95% CI) in the most conservative estimate to 6998-17,189 (6.69%-16.48%, 95% CI) in an estimate including variants with variable disease expressivity. Additionally, if the growth rate from the previous 4 yr continues, we estimate that the total number of disease-associated variants will grow 37% over the next 4 yr.
Figures
References
-
- Beskow LM, Burke W, Merz JF, Barr PA, Terry S, Penchaszadeh VB, Gostin LO, Gwinn M, Khoury MJ 2001. Informed consent for population-based research involving genetics. JAMA 286: 2315–2321 - PubMed
-
- Blow N 2009. Biobanking: freezer burn. Nat Methods 6: 173–178
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
