Characterization of a hierarchical network of hyaluronic acid/gelatin composite for use as a smart injectable biomaterial
- PMID: 22147507
- PMCID: PMC4490586
- DOI: 10.1002/mabi.201100335
Characterization of a hierarchical network of hyaluronic acid/gelatin composite for use as a smart injectable biomaterial
Abstract
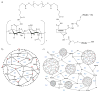
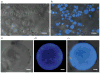
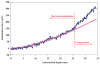
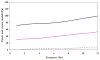
Hybrid HA/Ge hydrogel particles are embedded in a secondary HA network to improve their structural integrity. The internal microstructure of the particles is imaged through TEM. CSLM is used to identify the location of the Ge molecules in the microgels. Through indentation tests, the Young's modulus of the individual particles is found to be 22 ± 2.5 kPa. The overall shear modulus of the composite is 75 ± 15 Pa at 1 Hz. The mechanical properties of the substrate are found to be viable for cell adhesion. The particles' diameter at pH = 8 is twice that at pH = 5. The pH sensitivity is found to be appropriate for smart drug delivery. Based on their mechanical and structural properties, HA-Ge hierarchical materials may be well suited for use as injectable biomaterials for tissue reconstruction.
Copyright © 2012 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Viscoelasticity of hyaluronic acid-gelatin hydrogels for vocal fold tissue engineering.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2016 Feb;104(2):283-90. doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.33358. Epub 2015 Feb 27. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2016. PMID: 25728914 Free PMC article.
-
Hybrid Methacrylated Gelatin and Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogel Scaffolds. Preparation and Systematic Characterization for Prospective Tissue Engineering Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 23;22(13):6758. doi: 10.3390/ijms22136758. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34201769 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanical properties and in vitro behavior of nanofiber-hydrogel composites for tissue engineering applications.Nanotechnology. 2012 Mar 9;23(9):095705. doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/23/9/095705. Epub 2012 Feb 10. Nanotechnology. 2012. PMID: 22322583
-
Anatomy, molecular structures, and hyaluronic acid - Gelatin injectable hydrogels as a therapeutic alternative for hyaline cartilage recovery: A review.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2023 Sep;111(9):1705-1722. doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.35261. Epub 2023 May 13. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2023. PMID: 37178328 Review.
-
Hybrid Gelatin Hydrogels in Nanomedicine Applications.ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):2886-2906. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.0c01630. Epub 2021 Mar 9. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2021. PMID: 35014383 Review.
Cited by
-
Investigation of the Viability, Adhesion, and Migration of Human Fibroblasts in a Hyaluronic Acid/Gelatin Microgel-Reinforced Composite Hydrogel for Vocal Fold Tissue Regeneration.Adv Healthc Mater. 2016 Jan 21;5(2):255-65. doi: 10.1002/adhm.201500370. Epub 2015 Oct 26. Adv Healthc Mater. 2016. PMID: 26501384 Free PMC article.
-
Indentation of poroviscoelastic vocal fold tissue using an atomic force microscope.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2013 Dec;28:383-92. doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2013.05.026. Epub 2013 Jun 14. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2013. PMID: 23829979 Free PMC article.
-
Viscoelasticity of hyaluronic acid-gelatin hydrogels for vocal fold tissue engineering.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2016 Feb;104(2):283-90. doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.33358. Epub 2015 Feb 27. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2016. PMID: 25728914 Free PMC article.
-
Nonlinear laser scanning microscopy of human vocal folds.Laryngoscope. 2012 Feb;122(2):356-63. doi: 10.1002/lary.22460. Epub 2012 Jan 17. Laryngoscope. 2012. PMID: 22252839 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue engineering-based therapeutic strategies for vocal fold repair and regeneration.Biomaterials. 2016 Nov;108:91-110. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2016.08.054. Epub 2016 Sep 2. Biomaterials. 2016. PMID: 27619243 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

