Plasma half-life extension of small recombinant antibodies by fusion to immunoglobulin-binding domains
- PMID: 22147690
- PMCID: PMC3281650
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.311522
Plasma half-life extension of small recombinant antibodies by fusion to immunoglobulin-binding domains
Abstract
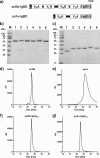
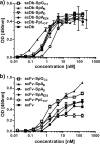
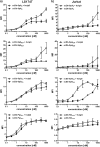
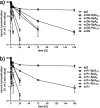
Many therapeutic proteins possessing a small size are rapidly cleared from circulation. Half-life extension strategies have therefore become increasingly important to improve the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of protein therapeutics. Here, we performed a comparative analysis of the half-life extension properties of various bacterial immunoglobulin-binding domains (IgBDs) derived from Staphylococcus protein A (SpA), Streptococcus protein G (SpG), and Finegoldia (formerly Peptostreptococcus) protein L (PpL). These domains, composed of 50-60 amino acid residues, were fused to the C terminus of a single-chain Fv and a bispecific single-chain diabody, respectively. All fusion proteins were produced in mammalian cells and retained their antigen-binding properties. The half-lives of the antibody molecules were prolonged to varying extents for the different IgBDs. The strongest effects in mice were observed for domain C3 of SpG (SpG(C3)) followed by domains B and D of SpA, suggesting that SpG(C3) is particularly useful to extend the plasma half-life of small proteins.
Figures
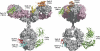
References
-
- Kontermann R. E. (2009) Strategies to extend plasma half-lives of recombinant antibodies. BioDrugs 23, 93–109 - PubMed
-
- Kontermann R. E. (2011) Strategies for extended serum half-life of protein therapeutics. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 22, 868–876 - PubMed
-
- Huang C. (2009) Receptor-Fc fusion therapeutics, traps, and MIMETIBODY technology. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 20, 692–699 - PubMed
-
- Chuang V. T., Kragh-Hansen U., Otagiri M. (2002) Pharmaceutical strategies utilizing recombinant human serum albumin. Pharm. Res. 19, 569–577 - PubMed
-
- Unverdorben F., Schwarz A., Richter F., Hutt M., Kontermann R. E. (2012) Half-life extension of a single-chain diabody by fusion to domain B of staphylococcal protein A. Protein Eng. Design Sel., in press - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

