C5a-regulated CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins β and δ are essential in Fcγ receptor-mediated inflammatory cytokine and chemokine production in macrophages
- PMID: 22147692
- PMCID: PMC3270976
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.280834
C5a-regulated CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins β and δ are essential in Fcγ receptor-mediated inflammatory cytokine and chemokine production in macrophages
Abstract
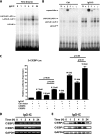
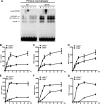
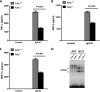
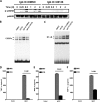
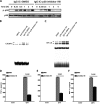
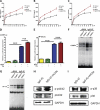
CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein β (C/EBPβ) and C/EBPδ are known to participate in the regulation of many genes associated with inflammation. However, little is known about the activation and function of C/EBPβ and -δ in inflammatory responses elicited by Fcγ receptor (FcγR) activation. Here we show that C/EBPβ and -δ activation are induced in IgG immune complex (IC)-treated macrophages. The increased expression of C/EBPβ and -δ occurred at both mRNA and protein levels. Furthermore, induction of C/EBPβ and -δ was mediated, to a large extent, by activating FcγRs. Using siRNA-mediated knockdown as well as macrophages deficient for C/EBPβ and/or -δ, we demonstrate that C/EBPβ and -δ play a critical role in the production of TNF-α, MIP-2, and MIP-1α in IgG IC-stimulated macrophages. Moreover, both ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK are involved in C/EBP induction and TNF-α, MIP-2, and MIP-1α production induced by IgG IC. We provide the evidence that C5a regulates IgG IC-induced inflammatory responses by enhancing ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK activities as well as C/EBPβ and -δ activities. Collectively, these data suggest that C/EBPβ and -δ are key regulators for FcγR-mediated induction of cytokines and chemokines in macrophages. Furthermore, C/EBPs may play an important regulatory role in IC-associated inflammatory responses.
Figures

References
-
- Nimmerjahn F., Ravetch J. V. (2008) Fcγ receptors as regulators of immune responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 8, 34–47 - PubMed
-
- Fernández N., Renedo M., García-Rodríguez C., Sánchez Crespo M. (2002) Activation of monocytic cells through Fc γ receptors induces the expression of macrophage-inflammatory protein (MIP)-1 α, MIP-1 β, and RANTES. J. Immunol. 169, 3321–3328 - PubMed
-
- Gao H., Neff T., Ward P. A. (2006) Regulation of lung inflammation in the model of IgG immune-complex injury. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 1, 215–242 - PubMed
-
- Bayón Y., Alonso A., Sánchez Crespo M. (1997) Stimulation of Fc γ receptors in rat peritoneal macrophages induces the expression of nitric oxide synthase and chemokines by mechanisms showing different sensitivities to antioxidants and nitric oxide donors. J. Immunol. 159, 887–894 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

