Second extracellular loop of human glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R) has a critical role in GLP-1 peptide binding and receptor activation
- PMID: 22147710
- PMCID: PMC3281720
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.309328
Second extracellular loop of human glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R) has a critical role in GLP-1 peptide binding and receptor activation
Abstract
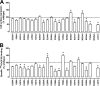
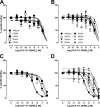
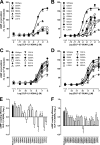
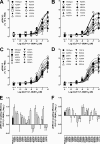
The glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R) is a therapeutically important family B G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that is pleiotropically coupled to multiple signaling effectors and, with actions including regulation of insulin biosynthesis and secretion, is one of the key targets in the management of type II diabetes mellitus. However, there is limited understanding of the role of the receptor core in orthosteric ligand binding and biological activity. To assess involvement of the extracellular loop (ECL) 2 in ligand-receptor interactions and receptor activation, we performed alanine scanning mutagenesis of loop residues and assessed the impact on receptor expression and GLP-1(1-36)-NH(2) or GLP-1(7-36)-NH(2) binding and activation of three physiologically relevant signaling pathways as follows: cAMP formation, intracellular Ca(2+) (Ca(2+)(i)) mobilization, and phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 (pERK1/2). Although antagonist peptide binding was unaltered, almost all mutations affected GLP-1 peptide agonist binding and/or coupling efficacy, indicating an important role in receptor activation. However, mutation of several residues displayed distinct pathway responses with respect to wild type receptor, including Arg-299 and Tyr-305, where mutation significantly enhanced both GLP-1(1-36)-NH(2)- and GLP-1(7-36)-NH(2)-mediated signaling bias for pERK1/2. In addition, mutation of Cys-296, Trp-297, Asn-300, Asn-302, and Leu-307 significantly increased GLP-1(7-36)-NH(2)-mediated signaling bias toward pERK1/2. Of all mutants studied, only mutation of Trp-306 to alanine abolished all biological activity. These data suggest a critical role of ECL2 of the GLP-1R in the activation transition(s) of the receptor and the importance of this region in the determination of both GLP-1 peptide- and pathway-specific effects.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Second extracellular loop of human glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R) differentially regulates orthosteric but not allosteric agonist binding and function.J Biol Chem. 2012 Feb 3;287(6):3659-73. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.309369. Epub 2011 Dec 6. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22147709 Free PMC article.
-
Differential impact of amino acid substitutions on critical residues of the human glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor involved in peptide activity and small-molecule allostery.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2015 Apr;353(1):52-63. doi: 10.1124/jpet.114.220913. Epub 2015 Jan 28. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2015. PMID: 25630467
-
Residues within the transmembrane domain of the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor involved in ligand binding and receptor activation: modelling the ligand-bound receptor.Mol Endocrinol. 2011 Oct;25(10):1804-18. doi: 10.1210/me.2011-1160. Epub 2011 Aug 25. Mol Endocrinol. 2011. PMID: 21868452 Free PMC article.
-
Minireview: Signal bias, allosterism, and polymorphic variation at the GLP-1R: implications for drug discovery.Mol Endocrinol. 2013 Aug;27(8):1234-44. doi: 10.1210/me.2013-1116. Epub 2013 Jul 17. Mol Endocrinol. 2013. PMID: 23864649 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The structure and function of the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor and its ligands.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 May;166(1):27-41. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01687.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 21950636 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ligand binding pocket formed by evolutionarily conserved residues in the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor core domain.J Biol Chem. 2015 Feb 27;290(9):5696-706. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.612606. Epub 2015 Jan 5. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25561730 Free PMC article.
-
Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 and Its Class B G Protein-Coupled Receptors: A Long March to Therapeutic Successes.Pharmacol Rev. 2016 Oct;68(4):954-1013. doi: 10.1124/pr.115.011395. Pharmacol Rev. 2016. PMID: 27630114 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetically encoded photocross-linkers determine the biological binding site of exendin-4 peptide in the N-terminal domain of the intact human glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R).J Biol Chem. 2017 Apr 28;292(17):7131-7144. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.779496. Epub 2017 Mar 10. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28283573 Free PMC article.
-
Incretin Mimetics as Rational Candidates for the Treatment of Traumatic Brain Injury.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2019 Apr 12;2(2):66-91. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.9b00003. Epub 2019 Feb 11. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2019. PMID: 31396586 Free PMC article.
-
Deconvoluting the Molecular Control of Binding and Signaling at the Amylin 3 Receptor: RAMP3 Alters Signal Propagation through Extracellular Loops of the Calcitonin Receptor.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2019 Mar 18;2(3):183-197. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.9b00010. eCollection 2019 Jun 14. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2019. PMID: 32219220 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Harmar A. J., Hills R. A., Rosser E. M., Jones M., Buneman O. P., Dunbar D. R., Greenhill S. D., Hale V. A., Sharman J. L., Bonner T. I., Catterall W. A., Davenport A. P., Delagrange P., Dollery C. T., Foord S. M., Gutman G. A., Laudet V., Neubig R. R., Ohlstein E. H., Olsen R. W., Peters J., Pin J. P., Ruffolo R. R., Searls D. B., Wright M. W., Spedding M. (2009) IUPHAR-DB. The IUPHAR database of G protein-coupled receptors and ion channels. Nucleic Acids Res. 37, D680–D685 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Overington J. P., Al-Lazikani B., Hopkins A. L. (2006) How many drug targets are there? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 5, 993–996 - PubMed
-
- Bazarsuren A., Grauschopf U., Wozny M., Reusch D., Hoffmann E., Schaefer W., Panzner S., Rudolph R. (2002) In vitro folding, functional characterization, and disulfide pattern of the extracellular domain of human GLP-1 receptor. Biophys. Chem. 96, 305–318 - PubMed
-
- Grauschopf U., Lilie H., Honold K., Wozny M., Reusch D., Esswein A., Schäfer W., Rücknagel K. P., Rudolph R. (2000) The N-terminal fragment of human parathyroid hormone receptor 1 constitutes a hormone binding domain and reveals a distinct disulfide pattern. Biochemistry 39, 8878–8887 - PubMed
-
- Bisello A., Adams A. E., Mierke D. F., Pellegrini M., Rosenblatt M., Suva L. J., Chorev M. (1998) Parathyroid hormone-receptor interactions identified directly by photocross-linking and molecular modeling studies. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 22498–22505 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

