Antitumor indolequinones induced apoptosis in human pancreatic cancer cells via inhibition of thioredoxin reductase and activation of redox signaling
- PMID: 22147753
- PMCID: PMC3286294
- DOI: 10.1124/mol.111.076091
Antitumor indolequinones induced apoptosis in human pancreatic cancer cells via inhibition of thioredoxin reductase and activation of redox signaling
Abstract
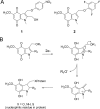
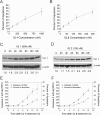
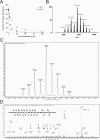
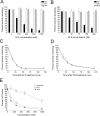
Indolequinones (IQs) were developed as potential antitumor agents against human pancreatic cancer. IQs exhibited potent antitumor activity against the human pancreatic cancer cell line MIA PaCa-2 with growth inhibitory IC(50) values in the low nanomolar range. IQs were found to induce time- and concentration-dependent apoptosis and to be potent inhibitors of thioredoxin reductase 1 (TR1) in MIA PaCa-2 cells at concentrations equivalent to those inducing growth-inhibitory effects. The mechanism of inhibition of TR1 by the IQs was studied in detail in cell-free systems using purified enzyme. The C-terminal selenocysteine of TR1 was characterized as the primary adduction site of the IQ-derived reactive iminium using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry analysis. Inhibition of TR1 by IQs in MIA PaCa-2 cells resulted in a shift of thioredoxin-1 redox state to the oxidized form and activation of the p38/c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase (JNK) mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway. Oxidized thioredoxin is known to activate apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1, an upstream activator of p38/JNK in the MAPK signaling cascade and this was confirmed in our study providing a potential mechanism for IQ-induced apoptosis. These data describe the redox and signaling events involved in the mechanism of growth inhibition induced by novel inhibitors of TR1 in human pancreatic cancer cells.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Potent activity of indolequinones against human pancreatic cancer: identification of thioredoxin reductase as a potential target.Mol Pharmacol. 2009 Jul;76(1):163-72. doi: 10.1124/mol.109.055855. Epub 2009 Apr 13. Mol Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19364812 Free PMC article.
-
Development of indolequinone mechanism-based inhibitors of NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1): NQO1 inhibition and growth inhibitory activity in human pancreatic MIA PaCa-2 cancer cells.Biochemistry. 2007 May 22;46(20):5941-50. doi: 10.1021/bi700008y. Epub 2007 Apr 25. Biochemistry. 2007. PMID: 17455910
-
Cytotoxic and radiosensitising effects of a novel thioredoxin reductase inhibitor in breast cancer.Invest New Drugs. 2021 Oct;39(5):1232-1241. doi: 10.1007/s10637-021-01106-5. Epub 2021 Mar 25. Invest New Drugs. 2021. PMID: 33768386 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of acrolein on the thioredoxin system: implications for redox-sensitive signaling.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2011 Sep;55(9):1361-74. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201100224. Epub 2011 Aug 3. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2011. PMID: 21812108 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selenium metabolism, selenoproteins and mechanisms of cancer prevention: complexities with thioredoxin reductase.Carcinogenesis. 1999 Sep;20(9):1657-66. doi: 10.1093/carcin/20.9.1657. Carcinogenesis. 1999. PMID: 10469608 Review.
Cited by
-
Thapsigargin sensitizes human esophageal cancer to TRAIL-induced apoptosis via AMPK activation.Sci Rep. 2016 Oct 12;6:35196. doi: 10.1038/srep35196. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27731378 Free PMC article.
-
Peperomin E and its orally bioavailable analog induce oxidative stress-mediated apoptosis of acute myeloid leukemia progenitor cells by targeting thioredoxin reductase.Redox Biol. 2019 Jun;24:101153. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2019.101153. Epub 2019 Mar 8. Redox Biol. 2019. PMID: 30909158 Free PMC article.
-
β2-AR-HIF-1α: a novel regulatory axis for stress-induced pancreatic tumor growth and angiogenesis.Curr Mol Med. 2013 Jul;13(6):1023-34. doi: 10.2174/15665240113139990055. Curr Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 23745588 Free PMC article.
-
The Thioredoxin System of Mammalian Cells and Its Modulators.Biomedicines. 2022 Jul 21;10(7):1757. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10071757. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35885063 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting mitochondria in cancer therapy could provide a basis for the selective anti-cancer activity.PLoS One. 2019 Mar 25;14(3):e0205623. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0205623. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30908483 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abate C, Patel L, Rauscher FJ, 3rd, Curran T. (1990) Redox regulation of fos and jun DNA-binding activity in vitro. Science 249:1157–1161 - PubMed
-
- Arnér ES, Holmgren A. (2006) The thioredoxin system in cancer. Semin Cancer Biol 16:420–426 - PubMed
-
- Berggren MI, Husbeck B, Samulitis B, Baker AF, Gallegos A, Powis G. (2001) Thioredoxin peroxidase-1 (peroxiredoxin-1) is increased in thioredoxin-1 transfected cells and results in enhanced protection against apoptosis caused by hydrogen peroxide but not by other agents including dexamethasone, etoposide, and doxorubicin. Arch Biochem Biophys 392:103–109 - PubMed
-
- Biswas S, Chida AS, Rahman I. (2006) Redox modifications of protein-thiols: emerging roles in cell signaling. Biochem Pharmacol 71:551–564 - PubMed
-
- Cassidy PB, Edes K, Nelson CC, Parsawar K, Fitzpatrick FA, Moos PJ. (2006) Thioredoxin reductase is required for the inactivation of tumor suppressor p53 and for apoptosis induced by endogenous electrophiles. Carcinogenesis 27:2538–2549 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

