Microbial infection-induced expansion of effector T cells overcomes the suppressive effects of regulatory T cells via an IL-2 deprivation mechanism
- PMID: 22147768
- PMCID: PMC3253229
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1100769
Microbial infection-induced expansion of effector T cells overcomes the suppressive effects of regulatory T cells via an IL-2 deprivation mechanism
Abstract
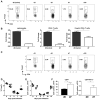
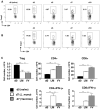
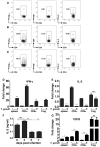
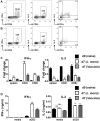
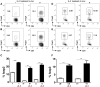
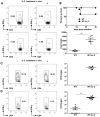
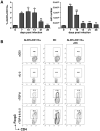
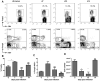
Foxp3(+) regulatory T (Treg) cells are a critical cell population that suppresses T cell activation in response to microbial and viral pathogens. We identify a cell-intrinsic mechanism by which effector CD4(+) T cells overcome the suppressive effects of Treg cells in the context of three distinct infections: Toxoplasma gondii, Listeria monocytogenes, and vaccinia virus. The acute responses to the parasitic, bacterial, and viral pathogens resulted in a transient reduction in frequency and absolute number of Treg cells. The infection-induced partial loss of Treg cells was essential for the initiation of potent Th1 responses and host protection against the pathogens. The observed disappearance of Treg cells was a result of insufficiency in IL-2 caused by the expansion of pathogen-specific CD4(+) T cells with a limited capacity of IL-2 production. Exogenous IL-2 treatment during the parasitic, bacterial, and viral infections completely prevented the loss of Treg cells, but restoration of Treg cells resulted in a greatly enhanced susceptibility to the pathogens. These results demonstrate that the transient reduction in Treg cells induced by pathogens via IL-2 deprivation is essential for optimal T cell responses and host resistance to microbial and viral pathogens.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Selective priming and expansion of antigen-specific Foxp3- CD4+ T cells during Listeria monocytogenes infection.J Immunol. 2009 Mar 1;182(5):3032-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0803402. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19234199 Free PMC article.
-
Essential role of IκBNS for in vivo CD4+ T-cell activation, proliferation, and Th1-cell differentiation during Listeria monocytogenes infection in mice.Eur J Immunol. 2019 Sep;49(9):1391-1398. doi: 10.1002/eji.201847961. Epub 2019 Jun 7. Eur J Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31049948 Free PMC article.
-
IL-2 contributes to maintaining a balance between CD4+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells and effector CD4+ T cells required for immune control of blood-stage malaria infection.J Immunol. 2011 Apr 15;186(8):4862-71. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1003777. Epub 2011 Mar 9. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21389253
-
Foxp3(+) regulatory T cells, immune stimulation and host defence against infection.Immunology. 2012 May;136(1):1-10. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2011.03551.x. Immunology. 2012. PMID: 22211994 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distinct regulatory CD4+T cell subsets; differences between naïve and antigen specific T regulatory cells.Curr Opin Immunol. 2011 Oct;23(5):641-7. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2011.07.012. Epub 2011 Aug 11. Curr Opin Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21840184 Review.
Cited by
-
Application of IL-2 therapy to target T regulatory cell function.Trends Immunol. 2012 Dec;33(12):626-32. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2012.07.007. Epub 2012 Aug 30. Trends Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22951308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Group 3 Innate Lymphoid Cell Defect in Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Deficient Mice Is Associated with T Cell Hyperactivation during Intestinal Infection.PLoS One. 2015 May 26;10(5):e0128335. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128335. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26010337 Free PMC article.
-
Avirulent Toxoplasma gondii generates therapeutic antitumor immunity by reversing immunosuppression in the ovarian cancer microenvironment.Cancer Res. 2013 Jul 1;73(13):3842-51. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-1974. Epub 2013 May 23. Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23704211 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Th17 cells by P. UF1 against systemic Listeria monocytogenes infection.Gut Microbes. 2018;9(3):279-287. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2017.1417731. Epub 2018 Feb 8. Gut Microbes. 2018. PMID: 29420115 Free PMC article.
-
Role of CD4+ Foxp3+ Regulatory T Cells in Protection Induced by a Live Attenuated, Replicating Type I Vaccine Strain of Toxoplasma gondii.Infect Immun. 2015 Sep;83(9):3601-11. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00217-15. Epub 2015 Jun 29. Infect Immun. 2015. PMID: 26123802 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sakaguchi S, Yamaguchi T, Nomura T, Ono M. Regulatory T cells and immune tolerance. Cell. 2008;133:775–787. - PubMed
-
- Fontenot JD, Rasmussen JP, Gavin MA, Rudensky AY. A function for interleukin 2 in Foxp3-expressing regulatory T cells. Nature Immunology. 2005;6:1142–1151. - PubMed
-
- Hori S, Nomura T, Sakaguchi S. Control of regulatory T cell development by the transcription factor Foxp3. Science. 2003;299:1057–1061. - PubMed
-
- Nishikawa H, Jager E, Ritter G, Old LJ, Gnjatic S. CD4(+) CD25(+) regulatory T cells control the induction of antigen-specific CD4(+) helper T cell responses in cancer patients. Blood. 2005;106:1008–1011. - PubMed
-
- Belkaid Y, Piccirillo CA, Mendez S, Shevach EM, Sacks DL. CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T cells control Leishmania major persistence and immunity. Nature. 2002;420:502–507. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

