Policy implications of adjusting randomized trial data for economic evaluations: a demonstration from the ASCUS-LSIL Triage Study
- PMID: 22147881
- PMCID: PMC3647223
- DOI: 10.1177/0272989X11428516
Policy implications of adjusting randomized trial data for economic evaluations: a demonstration from the ASCUS-LSIL Triage Study
Abstract
Background: Although the randomized controlled trial (RCT) is widely considered the most reliable method for evaluation of health care interventions, challenges to both internal and external validity exist. Thus, the efficacy of an intervention in a trial setting does not necessarily represent the real-world performance that decision makers seek to inform comparative effectiveness studies and economic evaluations.
Methods: Using data from the ASCUS-LSIL Triage Study (ALTS), we performed a simplified economic evaluation of age-based management strategies to detect cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade 3 (CIN3) among women who were referred to the study with low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (LSIL). We used data from the trial itself to adjust for 1) potential lead time bias and random error that led to variation in the observed prevalence of CIN3 by study arm and 2) potential ascertainment bias among providers in the most aggressive management arm.
Results: We found that using unadjusted RCT data may result in counterintuitive cost-effectiveness results when random error and/or bias are present. Following adjustment, the rank order of management strategies changed for 2 of the 3 age groups we considered.
Conclusions: Decision analysts need to examine study design, available trial data, and cost-effectiveness results closely in order to detect evidence of potential bias. Adjustment for random error and bias in RCTs may yield different policy conclusions relative to unadjusted trial data.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest. N.G.C.: No conflict. P.E.C. has received donations of HPV tests from Qiagen and serves on a data safety and monitoring committee for Merck, the manufacturer of Gardasil, for which he receives compensation. M.S.: No conflict. J.J.K.: No conflict.
Figures
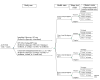
Comment in
-
Accounting for biases when linking empirical studies and simulation models.Med Decis Making. 2012 May-Jun;32(3):397-9. doi: 10.1177/0272989X12441398. Med Decis Making. 2012. PMID: 22593033 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Rittenhouse BE. The relevance of searching for effects under a clinical-trial lamppost: a key issue. Med Decis Making. 1995;14:348–357. - PubMed
-
- Rittenhouse BE. Exorcising protocol-induced spirits: making the clinical trial relevant for economics. Med Decis Making. 1997;17:331–339. - PubMed
-
- Drummond M. Experimental versus observational data in the economic evaluation of pharmaceuticals. Med Decis Making. 1998;18:512–518. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

