Pannexins in ischemia-induced neurodegeneration
- PMID: 22147915
- PMCID: PMC3251101
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1018262108
Pannexins in ischemia-induced neurodegeneration
Abstract
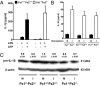
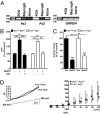
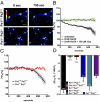
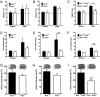
Pannexin 1 (Px1, Panx1) and pannexin 2 (Px2, Panx2) form large-pore nonselective channels in the plasma membrane of cells and were suggested to play a role in the pathophysiology of cerebral ischemia. To directly test a potential contribution of pannexins in ischemia-related mechanisms, we performed experiments in Px1(-/-), Px2(-/-), and Px1(-/-)Px2(-/-) knockout mice. IL-1β release, channel function in astrocytes, and cortical spreading depolarization were not altered in Px1(-/-)Px2(-/-) mice, indicating that, in contrast to previous concepts, these processes occur normally in the absence of pannexin channels. However, ischemia-induced dye release from cortical neurons was lower, indicating that channel function in Px1(-/-)Px2(-/-) neurons was impaired. Furthermore, Px1(-/-)Px2(-/-) mice had a better functional outcome and smaller infarcts than wild-type mice when subjected to ischemic stroke. In conclusion, our data demonstrate that Px1 and Px2 underlie channel function in neurons and contribute to ischemic brain damage.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- MacVicar BA, Thompson RJ. Non-junction functions of pannexin-1 channels. Trends Neurosci. 2010;33:93–102. - PubMed
-
- Lai CP, et al. Tumor-suppressive effects of pannexin 1 in C6 glioma cells. Cancer Res. 2007;67:1545–1554. - PubMed
-
- Bao L, Locovei S, Dahl G. Pannexin membrane channels are mechanosensitive conduits for ATP. FEBS Lett. 2004;572:65–68. - PubMed
-
- Barbe MT, Monyer H, Bruzzone R. Cell-cell communication beyond connexins: The pannexin channels. Physiology (Bethesda) 2006;21:103–114. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

