Lipopolysaccharide induces and activates the Nalp3 inflammasome in the liver
- PMID: 22147977
- PMCID: PMC3229625
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i43.4772
Lipopolysaccharide induces and activates the Nalp3 inflammasome in the liver
Abstract
Aim: To examine the activation of the Nalp3 inflammasome and its downstream targets following lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced stimulation in the liver.
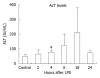
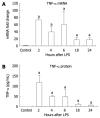
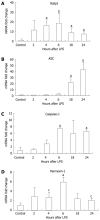
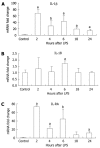
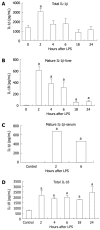
Methods: Six-to-eight-week-old C57BL/6 chow fed mice were injected intraperitoneally with 0.5 μg/g bodyweight LPS and sacrificed 2, 4, 6, 18 or 24 h later. LPS-induced liver damage was confirmed by a biochemical assay to detect alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels. To determine if LPS stimulation in the liver led to activation of the inflammasome, real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction was used to evaluate the mRNA expression of components of the Nalp3 inflammasome. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays were used to determine the protein expression levels of several downstream targets of the Nalp3 inflammasome, including caspase-1 and two cytokine targets of caspase-1, interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-18.
Results: We found that LPS injection resulted in liver damage as indicated by elevated ALT levels. This was associated with a significant increase in both mRNA and protein levels of the proinflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α in the liver, as well as increased levels of TNFs in serum. We showed that LPS stimulation led to upregulation of mRNA levels in the liver for all the receptor components of the inflammasome, including Nalp3, Nalp1, pannexin-1 and the adaptor molecule apoptosis-associated speck-like, caspase recruitment domain-domain containing protein. We also found increased levels of mRNA and protein for caspase-1, a downstream target of the inflammasome. In addition, LPS challenge led to increased levels of both mRNA and protein in the liver for two cytokine targets of caspase-1, IL-1β and IL-18. Interestingly, substantial baseline expression of pre-IL-1β and pre-IL-18 was found in the liver. Inflammasome and caspase-1 activation was indicated by the significant increase in the active forms of IL-1β and IL-18 after LPS stimulation.
Conclusion: Our results show that the Nalp3 inflammasome is upregulated and activated in the liver in response to LPS stimulation.
Keywords: Caspase-1; Endotoxin; Interleukin-18; Interleukin-1β; Nod-like receptor.
Figures
References
-
- Nath B, Szabo G. Alcohol-induced modulation of signaling pathways in liver parenchymal and nonparenchymal cells: implications for immunity. Semin Liver Dis. 2009;29:166–177. - PubMed
-
- Tilg H, Moschen AR, Kaser A. Obesity and the microbiota. Gastroenterology. 2009;136:1476–1483. - PubMed
-
- Ghanim H, Abuaysheh S, Sia CL, Korzeniewski K, Chaudhuri A, Fernandez-Real JM, Dandona P. Increase in plasma endotoxin concentrations and the expression of Toll-like receptors and suppressor of cytokine signaling-3 in mononuclear cells after a high-fat, high-carbohydrate meal: implications for insulin resistance. Diabetes Care. 2009;32:2281–2287. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Szabo G, Velayudham A, Romics L, Mandrekar P. Modulation of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis by pattern recognition receptors in mice: the role of toll-like receptors 2 and 4. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2005;29:140S–145S. - PubMed
-
- Miele L, Valenza V, La Torre G, Montalto M, Cammarota G, Ricci R, Mascianà R, Forgione A, Gabrieli ML, Perotti G, et al. Increased intestinal permeability and tight junction alterations in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2009;49:1877–1887. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

