Effects of CpG-ODNs on phenotype and function of monocyte-derived dendritic cells in chronic hepatitis B
- PMID: 22147985
- PMCID: PMC3229633
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i43.4825
Effects of CpG-ODNs on phenotype and function of monocyte-derived dendritic cells in chronic hepatitis B
Abstract
Aim: To study the effects of synthetic nonmethylated CpG-containing oligodeoxynucleotides (CpG-ODNs), either alone or combined with recombinant Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) polypeptide, on the phenotype, function, and intracellular signaling pathways of monocyte-derived dendritic cells (DCs) in patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB).
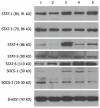
Methods: Peripheral blood monocytes isolated from CHB patients and healthy volunteers were induced to be dendritic cells by recombinant human granulocyte-monocyte colony stimulating factor and interleukin-4. The DCs were then treated with CpG-ODNs, CpG-ODNs/HBsAg, or tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α for 18 h. The expression of surface molecules including HLA-DR, CD86, and CD1a in DCs were detected by flow cytometry, and the expression of signal transducers and activators of transcription (STAT1, 3, 4, 5, 6) and suppressors of cell signaling (SOCS1, 3) were determined by Western blotting assay. In addition, the capacity of DCs to stimulate allogeneic T lymphocytes and the amount of IL-12p70 released from DCs were measured.
Results: In the DCs derived from patients with CHB, treatment with TNF-α, CpG-ODNs, or CpG-ODNs/HBsAg, as compared to the vector control, significantly increased the expression of HLA-DR, stimulated the release of IL-12p70, and enhanced the capacity of DCs to stimulate allogenic T lymphocytes. The expressions of STAT1/4/6 and SOCS1/3, but not STAT3/5, were upregulated by TNF-α, CpG-ODNs, and CpG-ODNs/HBsAg. In addition, the expression of CD1a was upregulated only in the presence of both CpG-ODNs and HBsAg.
Conclusion: The treatment with CpG-ODNs, either alone or combined with HBsAg, has a remarkable stimulatory effect on the impaired phenotype and function of DCs in CHB, possibly by regulating the expression of STAT1, 4, 6 and SOCS1, 3.
Keywords: Chronic hepatitis B; CpG oligodeoxynucleotides; Dendritic cell; Hepatitis B surface antigen; Signal transduction.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Effects of CpG-ODN combined with HBsAg on the phenotype, function and the activity of NF-kappa B and AP-1 of monocyte-derived dendritic cells in chronic hepatitis B patients].Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2008 Feb;16(2):97-100. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2008. PMID: 18304423 Chinese.
-
HBsAg loading on dendritic cells in patients with chronic hepatitis B: expressions of phenotypic molecules.Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2006 Feb;5(1):56-9. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2006. PMID: 16481284
-
Cutting edge: CpG oligonucleotides induce splenic CD19+ dendritic cells to acquire potent indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-dependent T cell regulatory functions via IFN Type 1 signaling.J Immunol. 2005 Nov 1;175(9):5601-5. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.175.9.5601. J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16237046
-
Effect of CpG motif containing oligodeoxynucleotides on dendritic cell function in patients with chronic hepatitis B.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2009 Jun;34(6):461-7. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2009. PMID: 19587425
-
CpG DNA as a vaccine adjuvant.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2011 Apr;10(4):499-511. doi: 10.1586/erv.10.174. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2011. PMID: 21506647 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Intramuscular primary immunization by nucleic acid vaccine pcDNA/Gpd-IL-2 and enhanced immunization with mucosal adjuvant CpG-ODN and Gpd-IL-2 recombinant protein effectively induced strong mucosal immune responses and immune protective effects against Treponema pallidum skin infection.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Mar;15(3):2533-2540. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.5689. Epub 2018 Jan 4. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 29456657 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into Immune Exhaustion in Chronic Hepatitis B: A Review of Checkpoint Receptor Expression.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Jul 21;17(7):964. doi: 10.3390/ph17070964. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39065812 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- van der Molen RG, Sprengers D, Binda RS, de Jong EC, Niesters HG, Kusters JG, Kwekkeboom J, Janssen HL. Functional impairment of myeloid and plasmacytoid dendritic cells of patients with chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2004;40:738–746. - PubMed
-
- Li RB, Chen HS, Cong X, Sun Jin, Wei L, Wang Y. Functions of cultured dendritic cells from patients with chronic hepatitis B decreased. Zhonghua Yixue Zazhi. 2002;82:887–890. - PubMed
-
- Gursel M, Verthelyi D, Klinman DM. CpG oligodeoxynucleotides induce human monocytes to mature into functional dendritic cells. Eur J Immunol. 2002;32:2617–2622. - PubMed
-
- Merad M, Sugie T, Engleman EG, Fong L. In vivo manipulation of dendritic cells to induce therapeutic immunity. Blood. 2002;99:1676–1682. - PubMed
-
- Pilon-Thomas S, Li W, Briggs JJ, Djeu J, Mulé JJ, Riker AI. Immunostimulatory effects of CpG-ODN upon dendritic cell-based immunotherapy in a murine melanoma model. J Immunother. 2006;29:381–387. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

