Credneramides A and B: neuromodulatory phenethylamine and isopentylamine derivatives of a vinyl chloride-containing fatty acid from cf. Trichodesmium sp. nov
- PMID: 22148360
- PMCID: PMC3336157
- DOI: 10.1021/np200611f
Credneramides A and B: neuromodulatory phenethylamine and isopentylamine derivatives of a vinyl chloride-containing fatty acid from cf. Trichodesmium sp. nov
Abstract
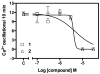
Credneramides A (1) and B (2), two vinyl chloride-containing metabolites, were isolated from a Papua New Guinea collection of cf. Trichodesmium sp. nov. and expand a recently described class of vinyl chloride-containing natural products. The precursor fatty acid, credneric acid (3), was isolated from both the aqueous and organic fractions of the parent fraction as well as from another geographically and phylogenetically distinct cyanobacterial collection (Panama). Credneramides A and B inhibited spontaneous calcium oscillations in murine cerebrocortical neurons at low micromolar concentrations (1, IC(50) 4.0 μM; 2, IC(50) 3.8 μM).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Biosynthetically intriguing chlorinated lipophilic metabolites from geographically distant tropical marine cyanobacteria.J Org Chem. 2012 May 4;77(9):4198-208. doi: 10.1021/jo300160e. Epub 2012 Apr 19. J Org Chem. 2012. PMID: 22489775 Free PMC article.
-
Hermitamides A and B, toxic malyngamide-type natural products from the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula.J Nat Prod. 2000 Jul;63(7):952-5. doi: 10.1021/np000037x. J Nat Prod. 2000. PMID: 10924172
-
Cobalt- versus ruthenium-catalyzed Alder-ene reaction for the synthesis of credneramide A and B.J Org Chem. 2012 Jun 1;77(11):5215-9. doi: 10.1021/jo3007896. Epub 2012 May 11. J Org Chem. 2012. PMID: 22568728
-
Pharmaceutical agents from filamentous marine cyanobacteria.Drug Discov Today. 2013 Sep;18(17-18):863-71. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2013.05.010. Epub 2013 May 25. Drug Discov Today. 2013. PMID: 23711931 Review.
-
Recent progress in neuroactive marine natural products.Nat Prod Rep. 2014 Jan 17;31(2):273-309. doi: 10.1039/c3np70083f. Nat Prod Rep. 2014. PMID: 24430532 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cycloaddition of cyclobutenone and azomethine imine enabled by chiral isothiourea organic catalysts.Chem Sci. 2015 Oct 1;6(10):6008-6012. doi: 10.1039/c5sc01972a. Epub 2015 Jul 20. Chem Sci. 2015. PMID: 29449914 Free PMC article.
-
Pitiamides A and B, Multifunctional Fatty Acid Amides from Marine Cyanobacteria.Planta Med. 2016 Jun;82(9-10):897-902. doi: 10.1055/s-0042-105157. Epub 2016 May 2. Planta Med. 2016. PMID: 27135625 Free PMC article.
-
Chlorinated Enyne Fatty Acid Amides from a Marine Cyanobacterium: Discovery of Taveuniamides L-M and Pharmacological Characterization of Taveuniamide F as a GPCR Antagonist with CNR1 Selectivity.Mar Drugs. 2023 Dec 30;22(1):28. doi: 10.3390/md22010028. Mar Drugs. 2023. PMID: 38248654 Free PMC article.
-
Phylogenetic inferences reveal a large extent of novel biodiversity in chemically rich tropical marine cyanobacteria.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013 Mar;79(6):1882-8. doi: 10.1128/AEM.03793-12. Epub 2013 Jan 11. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23315747 Free PMC article.
-
Calothrixamides A and B from the Cultured Cyanobacterium Calothrix sp. UIC 10520.J Nat Prod. 2018 Sep 28;81(9):2083-2090. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.8b00432. Epub 2018 Sep 7. J Nat Prod. 2018. PMID: 30192537 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gerwick WH, Tan LT, Sitachitta N. In: The Alkaloids. Cordell G, editor. Vol. 57. Academic Press; San Diego: 2001. pp. 75–184. Chapter 2. - PubMed
-
- Tidgewell K, Clark BR, Gerwick WH. In: Comprehensive Natural Products Chemistry. Mander L, Lui H-W, editors. Vol. 2. Elsevier; Oxford, UK: 2010. pp. 141–188. Ser.
-
- Edwards DJ, Marquez BL, Nogle LM, McPhail K, Goeger DE, Roberts MA, Gerwick WH. Chem Biol. 2004;11:817–833. - PubMed
-
- Berg KA, Lyra C, Sivonen K, Paulin L, Suomalainen S, Tuomi P, Rapala J. ISME J. 2009;3:314–325. - PubMed
-
- Garson MJ. In: Molluscs from Chemo-ecological Study to Biotechnological Application. Cimino G, Gavagnin M, editors. Springer-Verlag; Berlin, Heidelberg: 1996. pp. 159–174.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

