Effects of DNA methylation on the structure of nucleosomes
- PMID: 22148575
- PMCID: PMC3257366
- DOI: 10.1021/ja210273w
Effects of DNA methylation on the structure of nucleosomes
Abstract
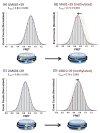
Nucleosomes are the fundamental packing units of the eukaryotic genome. Understanding the dynamic structure of a nucleosome is a key to the elucidation of genome packaging in eukaryotes, which is tied to the mechanisms of gene regulation. CpG methylation of DNA is an epigenetic modification associated with the inactivation of transcription and the formation of a repressive chromatin structure. Unraveling the changes in the structure of nucleosomes upon CpG methylation is an essential step toward the understanding of the mechanisms of gene repression and silencing by CpG methylation. Here we report single-molecule and ensemble fluorescence studies showing how the structure of a nucleosome is affected by CpG methylation. The results indicate that CpG methylation induces tighter wrapping of DNA around the histone core accompanied by a topology change. These findings suggest that changes in the physical properties of nucleosomes induced upon CpG methylation may contribute directly to the formation of a repressive chromatin structure.
© 2011 American Chemical Society
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

