Rapid reaction kinetics of proline dehydrogenase in the multifunctional proline utilization A protein
- PMID: 22148640
- PMCID: PMC3254707
- DOI: 10.1021/bi201603f
Rapid reaction kinetics of proline dehydrogenase in the multifunctional proline utilization A protein
Abstract
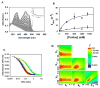
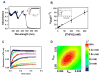
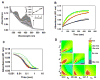
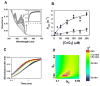
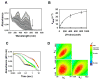
The multifunctional proline utilization A (PutA) flavoenzyme from Escherichia coli catalyzes the oxidation of proline to glutamate in two reaction steps using separate proline dehydrogenase (PRODH) and Δ(1)-pyrroline-5-carboxylate (P5C) dehydrogenase domains. Here, the kinetic mechanism of PRODH in PutA is studied by stopped-flow kinetics to determine microscopic rate constants for the proline:ubiquinone oxidoreductase mechanism. Stopped-flow data for proline reduction of the flavin cofactor (reductive half-reaction) and oxidation of reduced flavin by CoQ(1) (oxidative half-reaction) were best-fit by a double exponential from which maximum observable rate constants and apparent equilibrium dissociation constants were determined. Flavin semiquinone was not observed in the reductive or oxidative reactions. Microscopic rate constants for steps in the reductive and oxidative half-reactions were obtained by globally fitting the stopped-flow data to a simulated mechanism that includes a chemical step followed by an isomerization event. A microscopic rate constant of 27.5 s(-1) was determined for proline reduction of the flavin cofactor followed by an isomerization step of 2.2 s(-1). The isomerization step is proposed to report on a previously identified flavin-dependent conformational change [Zhang, W. et al. (2007) Biochemistry 46, 483-491] that is important for PutA functional switching but is not kinetically relevant to the in vitro mechanism. Using CoQ(1), a soluble analogue of ubiquinone, a rate constant of 5.4 s(-1) was obtained for the oxidation of flavin, thus indicating that this oxidative step is rate-limiting for k(cat) during catalytic turnover. Steady-state kinetic constants calculated from the microscopic rate constants agree with the experimental k(cat) and k(cat)/K(m) parameters.
Figures
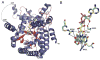


References
-
- Nakajima K, Natsu S, Mizote T, Nagata Y, Aoyania K, Fukuda Y, Nagata K. Possible involvement of putA gene in Helicobacter pylori colonization in the stomach and motility. Biomedical Research-Tokyo. 2008;29:9–18. - PubMed
-
- Nagata K, Nagata Y, Sato T, Fujino MA, Nakajima K, Tamura T. L-Serine, D- and L-proline and alanine as respiratory substrates of Helicobacter pylori: correlation between in vitro and in vivo amino acid levels. Microbiol. 2003;149:2023–2030. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

