Diagnosing ADHD in adolescence
- PMID: 22148878
- PMCID: PMC4085687
- DOI: 10.1037/a0026577
Diagnosing ADHD in adolescence
Abstract
Objective: This study examines adolescent-specific practical problems associated with current practice parameters for diagnosing attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) to inform recommendations for the diagnosis of ADHD in adolescents. Specifically, issues surrounding the use of self- versus informant ratings, diagnostic threshold, and retrospective reporting of childhood symptoms were addressed.
Method: Using data from the Pittsburgh ADHD Longitudinal Study (PALS), parent, teacher, and self-reports of symptoms and impairment were examined for 164 adolescents with a childhood diagnosis of ADHD (age M = 14.74 years) and 119 demographically similar non-ADHD controls (total N = 283).
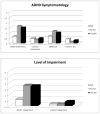
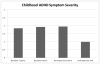
Results: Results indicated that 70% of the well-diagnosed childhood ADHD group continued to meet Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (4th ed., text rev.; American Psychiatric Association, 2000) diagnostic criteria for ADHD in adolescence; however, an additional 17% possessed clinically significant impairment in adolescence but did not qualify for a current ADHD diagnosis. The optimal source of information was combined reports from the parent and a core academic teacher. Adolescents with ADHD met criteria for very few symptoms of hyperactivity/impulsivity, suggesting a need to revisit the diagnostic threshold for these items. Additionally, emphasis on impairment, rather than symptom threshold, improved identification of adolescents with a gold-standard childhood diagnosis of ADHD and persistent ADHD symptoms. Parent retrospective reports of baseline functioning, but not adolescent self-reports, were significantly correlated with reports collected at baseline in childhood.
Conclusions: Recommendations are offered for diagnosing ADHD in adolescence based on these findings.
(PsycINFO Database Record (c) 2012 APA, all rights reserved).
Figures
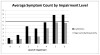
References
-
- American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry. Practice parameter for the assessement and treatment of children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry. 2007;46(7):894–921. - PubMed
-
- American Academy of Pediatrics. Clinical Practice Guideline: Treatment of the School-Aged Child with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Pediatrics. 2001;108:1033–1044. - PubMed
-
- Achenbach TM. Manual for the child behavior checklist/4-18 and 1991 profile. Burlington VT: Author; 1991.
-
- Achenbach TM, McConaughy SH, Howell CT. Child/adolescent behavioral and emotional problems: Implications of cross-informant correlations for situational specificity. Psychological Bulletin. 1987;101:213–232. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 4. Washington, DC: Author; 2000.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- N01 MH012010/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA012414/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH069614/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- ES0515-08/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- DA05605/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA012342/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 DA005605/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R29 MH047390/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH045576/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH050467/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- DA12414/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K21 AA000202/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- F31 DA017546/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- MH48157/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH053554/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA000626/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AA008746/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- AA11873/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- AA06267/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA011873/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- MH53554/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- AA12342/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AA011873/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- AA08746/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AA011873/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- MH069614/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

