Cancer cell signaling pathways targeted by spice-derived nutraceuticals
- PMID: 22149093
- PMCID: PMC3645308
- DOI: 10.1080/01635581.2012.630551
Cancer cell signaling pathways targeted by spice-derived nutraceuticals
Abstract
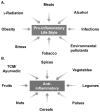
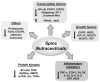
Extensive research within the last half a century has revealed that cancer is caused by dysregulation of as many as 500 different gene products. Most natural products target multiple gene products and thus are ideally suited for prevention and treatment of various chronic diseases, including cancer. Dietary agents such as spices have been used extensively in the Eastern world for a variety of ailments for millennia, and five centuries ago they took a golden journey to the Western world. Various spice-derived nutraceuticals, including 1'-acetoxychavicol acetate, anethole, capsaicin, cardamonin, curcumin, dibenzoylmethane, diosgenin, eugenol, gambogic acid, gingerol, thymoquinone, ursolic acid, xanthohumol, and zerumbone derived from galangal, anise, red chili, black cardamom, turmeric, licorice, fenugreek, clove, kokum, ginger, black cumin, rosemary, hop, and pinecone ginger, respectively, are the focus of this review. The modulation of various transcription factors, growth factors, protein kinases, and inflammatory mediators by these spice-derived nutraceuticals are described. The anticancer potential through the modulation of various targets is also the subject of this review. Although they have always been used to improve taste and color and as a preservative, they are now also used for prevention and treatment of a wide variety of chronic inflammatory diseases, including cancer.
Figures

References
-
- Kamb A, Wee S, Lengauer C. Why is cancer drug discovery so difficult? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2007;6:115–120. - PubMed
-
- Knowles J, Gromo G. A guide to drug discovery: target selection in drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2003;2:63–69. - PubMed
-
- Aggarwal BB, Sethi G, Baladandayuthapani V, Krishnan S, Shishodia S. Targeting cell signaling pathways for drug discovery: an old lock needs a new key. J Cell Biochem. 2007;102:580–592. - PubMed
-
- Fojo T, Parkinson DR. Biologically targeted cancer therapy and marginal benefits: are we making too much of too little or are we achieving too little by giving too much? Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16:5972–5980. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
