SPANosomes as delivery vehicles for small interfering RNA (siRNA)
- PMID: 22149175
- PMCID: PMC3273546
- DOI: 10.1021/mp200426h
SPANosomes as delivery vehicles for small interfering RNA (siRNA)
Abstract
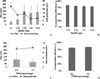
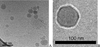
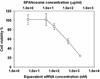
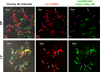
Nonionic surfactant vesicles, or SPANosomes (SPs), comprised of cationic lipid and sorbitan monooleate (Span 80) were synthesized and evaluated as small interfering RNA (siRNA) vectors. The SPs had a mean diameter of less than 100 nm and exhibited excellent colloidal stability. The SP/siRNA complexes possessed a slightly positive zeta potential of 12 mV and demonstrated a high siRNA incorporation efficiency of greater than 80%. Cryogenic transmission electron microscopy (cryo-TEM) imaging of the SP/siRNA indicated a predominantly core-shell structure. The SP/siRNA complexes were shown to efficiently and specifically silence expression of both green fluorescent protein (GFP) (66% knockdown) and aromatase (77% knockdown) genes in breast cancer cell lines. In addition, the cellular trafficking pathway of the SP/siRNA was investigated by confocal microscopy using molecular beacons as probes for cytosolic delivery. The results showed efficient endosomal escape and cytosolic delivery of the siRNA cargo following internalization of the SP/siRNA complexes. In conclusion, Span 80 is a potent helper lipid, and the SPs are promising vehicles for siRNA delivery.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Lipoplexes versus nanoparticles: pDNA/siRNA delivery.Drug Deliv. 2013 Feb;20(2):57-64. doi: 10.3109/10717544.2012.752419. Drug Deliv. 2013. PMID: 23537464
-
siRNA delivery by a transferrin-associated lipid-based vector: a non-viral strategy to mediate gene silencing.J Gene Med. 2007 Mar;9(3):170-83. doi: 10.1002/jgm.1006. J Gene Med. 2007. PMID: 17351968
-
Quantitative silencing of EGFP reporter gene by self-assembled siRNA lipoplexes of LinOS and cholesterol.Mol Pharm. 2012 Nov 5;9(11):3384-95. doi: 10.1021/mp300435x. Epub 2012 Oct 25. Mol Pharm. 2012. PMID: 23057412 Free PMC article.
-
Design of Ionizable Lipids To Overcome the Limiting Step of Endosomal Escape: Application in the Intracellular Delivery of mRNA, DNA, and siRNA.J Med Chem. 2016 Apr 14;59(7):3046-62. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b01679. Epub 2016 Mar 17. J Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 26943260
-
Effect of surface properties on liposomal siRNA delivery.Biomaterials. 2016 Feb;79:56-68. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.11.056. Epub 2015 Dec 2. Biomaterials. 2016. PMID: 26695117 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative cellular pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of siRNA delivery by SPANosomes and by cationic liposomes.Nanomedicine. 2013 May;9(4):504-13. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2012.10.002. Epub 2012 Oct 29. Nanomedicine. 2013. PMID: 23117046 Free PMC article.
-
Cationic Niosomes as Non-Viral Vehicles for Nucleic Acids: Challenges and Opportunities in Gene Delivery.Pharmaceutics. 2019 Jan 22;11(2):50. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics11020050. Pharmaceutics. 2019. PMID: 30678296 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preclinical testing of antiviral siRNA therapeutics delivered in lipid nanoparticles in animal models - a comprehensive review.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2025 Feb 25. doi: 10.1007/s13346-025-01815-x. Online ahead of print. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2025. PMID: 40000558
-
Advances and prospects of RNA delivery nanoplatforms for cancer therapy.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2025 Jan;15(1):52-96. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2024.09.009. Epub 2024 Sep 14. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2025. PMID: 40041887 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel lipoidal amine-based nanocarrier formulations for siRNA delivery.Ther Deliv. 2012 Jun;3(6):715-23. doi: 10.4155/tde.12.47. Ther Deliv. 2012. PMID: 22838067 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akinc A, Zumbuehl A, Goldberg M, Leshchiner ES, Busini V, Hossain N, Bacallado SA, Nguyen DN, Fuller J, Alvarez R, Borodovsky A, Borland T, Constien R, de Fougerolles A, Dorkin JR, Narayanannair Jayaprakash K, Jayaraman M, John M, Koteliansky V, Manoharan M, Nechev L, Qin J, Racie T, Raitcheva D, Rajeev KG, Sah DW, Soutschek J, Toudjarska I, Vornlocher HP, Zimmermann TS, Langer R, Anderson DG. A combinatorial library of lipid-like materials for delivery of RNAi therapeutics. Nat Biotechnol. 2008;26(5):561–569. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Palliser D, Chowdhury D, Wang QY, Lee SJ, Bronson RT, Knipe DM, Lieberman J. An siRNA-based microbicide protects mice from lethal herpes simplex virus 2 infection. Nature. 2006;439(7072):89–94. - PubMed
-
- Dykxhoorn DM, Palliser D, Lieberman J. The silent treatment: siRNAs as small molecule drugs. Gene Ther. 2006;13(6):541–552. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

