Effects of maxillary molar distalization with Zygoma-Gear Appliance
- PMID: 22149541
- PMCID: PMC8845558
- DOI: 10.2319/091611-595.1
Effects of maxillary molar distalization with Zygoma-Gear Appliance
Abstract
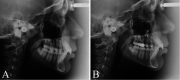
Objective: To evaluate the dentoalveolar, skeletal, and soft tissue effects of the Zygoma-Gear Appliance (ZGA) when used for bilateral distalization of the maxillary molars.
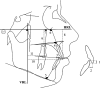
Materials and methods: The study group included 15 patients (mean age, 15.87 ± 1.09 years; range: 14-18 years) treated with the ZGA system supported with zygomatic anchorage miniplates. The changes due to the distalization were evaluated from the lateral cephalometric films taken before and after distalization by means of a paired t-test.
Results: The mean treatment period required to achieve a Class I molar relationship was 5.21 months. The distalization amount of the maxillary molars was 4.37 ± 2.15 mm (P < .001), and, thus, the rate for the distal movement of the molars was 0.84 mm per month. Maxillary first molars showed a slight intrusion (0.50 mm) (P > .05), while distal tipping was only 3.30° ± 2.31° (P > .05). Furthermore, there was a decrease in overjet (-0.50 mm) (P > .05), indicating that there was no anchorage loss with use of the ZGA.
Conclusions: Maxillary molar distalization without anchorage loss can be achieved in a short time with ZGA.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Analysis of the efficacy of conventional, skeletal and invisible orthodontic appliance for upper molar distalization in Class II Malocclusion patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Oral Health. 2025 Sep 2;25(1):1396. doi: 10.1186/s12903-025-06378-4. BMC Oral Health. 2025. PMID: 40898166 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of zygoma-gear appliance for unilateral maxillary molar distalization: A prospective clinical study.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2016 Dec;150(6):989-996. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2016.05.010. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2016. PMID: 27894548
-
Unilateral maxillary molar distalization with zygoma-gear appliance.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2012 Aug;142(2):e1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2012.02.026. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2012. PMID: 22858341
-
Bilateral distalization of maxillary first molars in a group of adult patients after extraction of maxillary second molars using infra-zygomatic mini-implants: A prospective clinical trial.J World Fed Orthod. 2024 Aug;13(4):155-161. doi: 10.1016/j.ejwf.2024.03.005. Epub 2024 Apr 11. J World Fed Orthod. 2024. PMID: 38609801 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of skeletal anchorage distalizers effect in maxillary buccal segment: A systematic review.Stomatologija. 2018;20(3):66-72. Stomatologija. 2018. PMID: 30531160
Cited by
-
Analysis of midpalatal miniscrew-assisted maxillary molar distalization patterns with simultaneous use of fixed appliances: A preliminary study.Korean J Orthod. 2016 Jan;46(1):55-61. doi: 10.4041/kjod.2016.46.1.55. Epub 2016 Jan 25. Korean J Orthod. 2016. PMID: 26877983 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the efficacy of conventional, skeletal and invisible orthodontic appliance for upper molar distalization in Class II Malocclusion patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Oral Health. 2025 Sep 2;25(1):1396. doi: 10.1186/s12903-025-06378-4. BMC Oral Health. 2025. PMID: 40898166 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of miniscrew-supported maxillary molar distalization according to temporary anchorage device features and appliance design: systematic review and meta-analysis.Angle Orthod. 2024 Jan 1;94(1):107-121. doi: 10.2319/052223-364.1. Angle Orthod. 2024. PMID: 37870251 Free PMC article.
-
The Use of Mini-Plates for the Treatment of a High-Angle, Dual Bite, Class II Malocclusion.Turk J Orthod. 2019 Mar;32(1):52-58. doi: 10.5152/TurkJOrthod.2018.18029. Epub 2019 Jan 8. Turk J Orthod. 2019. PMID: 30944901 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment effects of skeletally anchored Forsus FRD EZ and Herbst appliances: A retrospective clinical study.Angle Orthod. 2016 Mar;86(2):306-14. doi: 10.2319/040315-225.1. Epub 2015 Aug 10. Angle Orthod. 2016. PMID: 26258899 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nalcaci R, Biçakçi A. A, Ozan F. Noncompliance screw supported maxillary molar distalization in a parallel manner. Korean J Orthod. 2010;40:250–259.
-
- Baldini G. Unilateral headgear: lateral forces as unavoidable side effects. Am J Orthod. 1980;77:333–340. - PubMed
-
- Keles A. Maxillary unilateral molar distalization with sliding mechanics: a preliminary investigation. Eur J Orthod. 2001;23:507–515. - PubMed
-
- Bondemark L, Kurol J, Bernhold M. Repelling magnets versus superelastic nickel-titanium coils in simultaneous distal movement of maxillary first and second molars. Angle Orthod. 1994;64:189–198. - PubMed
-
- Keim R. G, Berkman C. Intra-arch maxillary molar distalization appliances for Class II correction. J Clin Orthod. 2004;38:505–511. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

