Effects of exposure equalization on image signal-to-noise ratios in digital mammography: a simulation study with an anthropomorphic breast phantom
- PMID: 22149832
- PMCID: PMC3247925
- DOI: 10.1118/1.3659709
Effects of exposure equalization on image signal-to-noise ratios in digital mammography: a simulation study with an anthropomorphic breast phantom
Abstract
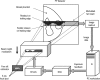
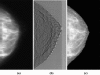
Purpose: The scan equalization digital mammography (SEDM) technique combines slot scanning and exposure equalization to improve low-contrast performance of digital mammography in dense tissue areas. In this study, full-field digital mammography (FFDM) images of an anthropomorphic breast phantom acquired with an anti-scatter grid at various exposure levels were superimposed to simulate SEDM images and investigate the improvement of low-contrast performance as quantified by primary signal-to-noise ratios (PSNRs).
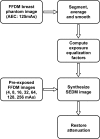
Methods: We imaged an anthropomorphic breast phantom (Gammex 169 "Rachel," Gammex RMI, Middleton, WI) at various exposure levels using a FFDM system (Senographe 2000D, GE Medical Systems, Milwaukee, WI). The exposure equalization factors were computed based on a standard FFDM image acquired in the automatic exposure control (AEC) mode. The equalized image was simulated and constructed by superimposing a selected set of FFDM images acquired at 2, 1, 1/2, 1/4, 1/8, 1/16, and 1/32 times of exposure levels to the standard AEC timed technique (125 mAs) using the equalization factors computed for each region. Finally, the equalized image was renormalized regionally with the exposure equalization factors to result in an appearance similar to that with standard digital mammography. Two sets of FFDM images were acquired to allow for two identically, but independently, formed equalized images to be subtracted from each other to estimate the noise levels. Similarly, two identically but independently acquired standard FFDM images were subtracted to estimate the noise levels. Corrections were applied to remove the excess system noise accumulated during image superimposition in forming the equalized image. PSNRs over the compressed area of breast phantom were computed and used to quantitatively study the effects of exposure equalization on low-contrast performance in digital mammography.
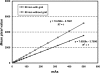
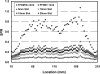
Results: We found that the highest achievable PSNR improvement factor was 1.89 for the anthropomorphic breast phantom used in this study. The overall PSNRs were measured to be 79.6 for the FFDM imaging and 107.6 for the simulated SEDM imaging on average in the compressed area of breast phantom, resulting in an average improvement of PSNR by ∼35% with exposure equalization. We also found that the PSNRs appeared to be largely uniform with exposure equalization, and the standard deviations of PSNRs were estimated to be 10.3 and 7.9 for the FFDM imaging and the simulated SEDM imaging, respectively. The average glandular dose for SEDM was estimated to be 212.5 mrad, ∼34% lower than that of standard AEC-timed FFDM (323.8 mrad) as a result of exposure equalization for the entire breast phantom.
Conclusions: Exposure equalization was found to substantially improve image PSNRs in dense tissue regions and result in more uniform image PSNRs. This improvement may lead to better low-contrast performance in detecting and visualizing soft tissue masses and micro-calcifications in dense tissue areas for breast imaging tasks.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Evaluation of clinical full field digital mammography with the task specific system-model-based Fourier Hotelling observer (SMFHO) SNR.Med Phys. 2014 May;41(5):051907. doi: 10.1118/1.4870377. Med Phys. 2014. PMID: 24784386
-
Comparison of scatter rejection and low-contrast performance of scan equalization digital radiography (SEDR), slot-scan digital radiography, and full-field digital radiography systems for chest phantom imaging.Med Phys. 2011 Jan;38(1):23-33. doi: 10.1118/1.3519903. Med Phys. 2011. PMID: 21361171 Free PMC article.
-
Noise equalization for detection of microcalcification clusters in direct digital mammogram images.IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2004 Mar;23(3):313-20. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2004.824240. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2004. PMID: 15027524 Clinical Trial.
-
Digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT): a review of the evidence for use as a screening tool.Clin Radiol. 2016 Feb;71(2):141-50. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2015.11.008. Epub 2015 Dec 23. Clin Radiol. 2016. PMID: 26707815 Review.
-
Synthesized Digital Mammography Imaging.Radiol Clin North Am. 2017 May;55(3):503-512. doi: 10.1016/j.rcl.2016.12.005. Epub 2017 Feb 14. Radiol Clin North Am. 2017. PMID: 28411676 Review.
Cited by
-
The Integration of Micro-CT Imaging and Finite Element Simulations for Modelling Tooth-Inlay Systems for Mechanical Stress Analysis: A Preliminary Study.J Funct Biomater. 2025 Jul 21;16(7):267. doi: 10.3390/jfb16070267. J Funct Biomater. 2025. PMID: 40710481 Free PMC article.
-
Using aluminum for scatter control in mammography: preliminary work using measurements of CNR and FOM.Radiol Phys Technol. 2020 Mar;13(1):37-44. doi: 10.1007/s12194-019-00545-3. Epub 2019 Nov 20. Radiol Phys Technol. 2020. PMID: 31749130
-
Variation in digital breast tomosynthesis image quality at differing heights above the detector.J Med Radiat Sci. 2022 Jun;69(2):174-181. doi: 10.1002/jmrs.565. Epub 2021 Dec 27. J Med Radiat Sci. 2022. PMID: 34957671 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Breast Cancer Facts & Figures 2009–2010, http://www.cancer.org/Research/CancerFactsFigures/BreastCancerFactsFigur....
-
- Vacek P. M. and Geller B. M., “A prospective study of breast cancer risk using routine mammographic breast density measurements,” Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 13, 715–722 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Lam K. L. and Chan H.-P., “Development of x-ray beam equalization technique in mammography,” Radiology 169(P), 338 (1988).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

