Genetic evidence for natural product-mediated plant-plant allelopathy in rice (Oryza sativa)
- PMID: 22150231
- PMCID: PMC3257406
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2011.04005.x
Genetic evidence for natural product-mediated plant-plant allelopathy in rice (Oryza sativa)
Abstract
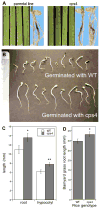
• There is controversy as to whether specific natural products play a role in directly mediating antagonistic plant-plant interactions - that is, allelopathy. If proved to exist, such phenomena would hold considerable promise for agronomic improvement of staple food crops such as rice (Oryza sativa). • However, while substantiated by the presence of phytotoxic compounds at potentially relevant concentrations, demonstrating a direct role for specific natural products in allelopathy has been difficult because of the chemical complexity of root and plant litter exudates. This complexity can be bypassed via selective genetic manipulation to ablate production of putative allelopathic compounds, but such an approach previously has not been applied. • The rice diterpenoid momilactones provide an example of natural products for which correlative biochemical evidence has been obtained for a role in allelopathy. Here, we apply reverse genetics, using knock-outs of the relevant diterpene synthases (copalyl diphosphate synthase 4 (OsCPS4) and kaurene synthase-like 4 (OsKSL4)), to demonstrate that rice momilactones are involved in allelopathy, including suppressing growth of the widespread rice paddy weed, barnyard grass (Echinochloa crus-galli). • Thus, our results not only provide novel genetic evidence for natural product-mediated allelopathy, but also furnish a molecular target for breeding and metabolic engineering of this important crop plant.
© 2011 The Authors. New Phytologist © 2011 New Phytologist Trust.
Figures




References
-
- Bais HP, Vepachedu R, Gilroy S, Callaway RM, Vivanco JM. Allelopathy and exotic plant invasion: from molecules and genes to species interactions. Science. 2003;301(5638):1377–1380. - PubMed
-
- Belz RG. Allelopathy in crop/weed interactions--an update. Pest Manag Sci. 2007;63(4):308–326. - PubMed
-
- Cartwright DW, Langcake P, Pryce RJ, Leworthy DP, Ride JP. Chemical activation of host defence mechanisms as a basis for crop protection. Nature. 1977;267:511–513.
-
- Cartwright DW, Langcake P, Pryce RJ, Leworthy DP, Ride JP. Isolation and characterization of two phytoalexins from rice as momilactones A and B. Phytochemistry. 1981;20:535–537.
-
- Chu HY, Wegel E, Osbourn A. From hormones to secondary metabolism: the emergence of metabolic gene clusters in plants. The Plant journal : for cell and molecular biology. 2011;66 (1):66–79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

