Mixed electrical-chemical transmission between hippocampal mossy fibers and pyramidal cells
- PMID: 22151275
- PMCID: PMC3251635
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2011.07930.x
Mixed electrical-chemical transmission between hippocampal mossy fibers and pyramidal cells
Abstract
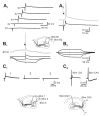
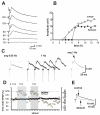
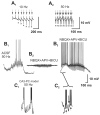
Morphological and electrophysiological studies have shown that granule cell axons, the mossy fibers (MFs), establish gap junctions and therefore electrical communication among them. That granule cells express gap junctional proteins in their axons suggests the possibility that their terminals also express them. If this were to be the case, mixed electrical-chemical communication could be supported, as MF terminals normally use glutamate for fast communication with their target cells. Here we present electrophysiological studies in the rat and modeling studies consistent with this hypothesis. We show that MF activation produced fast spikelets followed by excitatory postsynaptic potentials in pyramidal cells (PCs), which, unlike the spikelets, underwent frequency potentiation and were strongly depressed by activation of metabotropic glutamate receptors, as expected from transmission of MF origin. The spikelets, which persisted during blockade of chemical transmission, were potentiated by dopamine and suppressed by the gap junction blocker carbenoxolone. The various waveforms evoked by MF stimulation were replicated in a multi-compartment model of a PC by brief current-pulse injections into the proximal apical dendritic compartment, where MFs are known to contact PCs. Mixed electrical and glutamatergic communication between granule cells and some PCs in CA3 may ensure the activation of sets of PCs, bypassing the strong action of concurrent feed-forward inhibition that granule cells activate. Importantly, MF-to-PC electrical coupling may allow bidirectional, possibly graded, communication that can be faster than chemical synapses and subject to different forms of modulation.
© 2011 The Authors. European Journal of Neuroscience © 2011 Federation of European Neuroscience Societies and Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mixed neurotransmission in the hippocampal mossy fibers.Front Cell Neurosci. 2013 Nov 22;7:210. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2013.00210. Front Cell Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24319410 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cocultures of GFP(+) -granule cells with GFP(-) -pyramidal cells and interneurons for the study of mossy fiber neurotransmission with paired recordings.Hippocampus. 2013 Apr;23(4):247-52. doi: 10.1002/hipo.22102. Epub 2013 Feb 25. Hippocampus. 2013. PMID: 23436451
-
Dissociation of CA3 pyramidal cells with attached, functional, identified mossy fiber and interneuronal boutons for studying glutamatergic and GABAergic synaptic transmission.J Neurosci Methods. 2012 Jul 15;208(2):155-60. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2012.05.012. Epub 2012 May 23. J Neurosci Methods. 2012. PMID: 22633895
-
GABAergic signaling at mossy fiber synapses in neonatal rat hippocampus.J Neurosci. 2006 Jan 11;26(2):597-608. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4493-05.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16407558 Free PMC article.
-
Role of giant depolarizing potentials in shaping synaptic currents in the developing hippocampus.Crit Rev Neurobiol. 2006;18(1-2):13-23. doi: 10.1615/critrevneurobiol.v18.i1-2.30. Crit Rev Neurobiol. 2006. PMID: 17725505 Review.
Cited by
-
Mixed Electrical-Chemical Synapses in Adult Rat Hippocampus are Primarily Glutamatergic and Coupled by Connexin-36.Front Neuroanat. 2012 May 15;6:13. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2012.00013. eCollection 2012. Front Neuroanat. 2012. PMID: 22615687 Free PMC article.
-
Axonal properties determine somatic firing in a model of in vitro CA1 hippocampal sharp wave/ripples and persistent gamma oscillations.Eur J Neurosci. 2012 Sep;36(5):2650-60. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2012.08184.x. Epub 2012 Jun 15. Eur J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22697272 Free PMC article.
-
Connexin36 identified at morphologically mixed chemical/electrical synapses on trigeminal motoneurons and at primary afferent terminals on spinal cord neurons in adult mouse and rat.Neuroscience. 2014 Mar 28;263:159-80. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.12.057. Epub 2014 Jan 7. Neuroscience. 2014. PMID: 24406437 Free PMC article.
-
Mixed neurotransmission in the hippocampal mossy fibers.Front Cell Neurosci. 2013 Nov 22;7:210. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2013.00210. Front Cell Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24319410 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Motor neurons control locomotor circuit function retrogradely via gap junctions.Nature. 2016 Jan 21;529(7586):399-402. doi: 10.1038/nature16497. Epub 2016 Jan 13. Nature. 2016. PMID: 26760208
References
-
- Alle H, Geiger JR. Combined analog and action potential coding in hippocampal mossy fibers. Science. 2006;311:1290–1293. - PubMed
-
- Bennett MVL, Zukin RS. Electrical coupling and neuronal synchronization in the mammalian brain. Neuron. 2004;41:495–511. - PubMed
-
- Bischofberger J, Engel D, Li L, Geiger JR, Jonas P. Patch-clamp recording from mossy fiber terminals in hippocampal slices. Nat. Protoc. 2006;1:2075–2081. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

