Accelerated large-scale multiple sequence alignment
- PMID: 22151470
- PMCID: PMC3310909
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-12-466
Accelerated large-scale multiple sequence alignment
Abstract
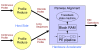
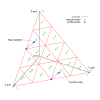
Background: Multiple sequence alignment (MSA) is a fundamental analysis method used in bioinformatics and many comparative genomic applications. Prior MSA acceleration attempts with reconfigurable computing have only addressed the first stage of progressive alignment and consequently exhibit performance limitations according to Amdahl's Law. This work is the first known to accelerate the third stage of progressive alignment on reconfigurable hardware.
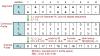
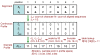
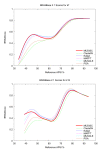
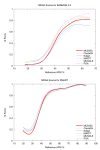
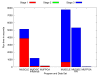
Results: We reduce subgroups of aligned sequences into discrete profiles before they are pairwise aligned on the accelerator. Using an FPGA accelerator, an overall speedup of up to 150 has been demonstrated on a large data set when compared to a 2.4 GHz Core2 processor.
Conclusions: Our parallel algorithm and architecture accelerates large-scale MSA with reconfigurable computing and allows researchers to solve the larger problems that confront biologists today. Program source is available from http://dna.cs.byu.edu/msa/.
Figures





Similar articles
-
CMSA: a heterogeneous CPU/GPU computing system for multiple similar RNA/DNA sequence alignment.BMC Bioinformatics. 2017 Jun 24;18(1):315. doi: 10.1186/s12859-017-1725-6. BMC Bioinformatics. 2017. PMID: 28646874 Free PMC article.
-
Segment-based multiple sequence alignment.Bioinformatics. 2008 Aug 15;24(16):i187-92. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btn281. Bioinformatics. 2008. PMID: 18689823
-
Improvement in accuracy of multiple sequence alignment using novel group-to-group sequence alignment algorithm with piecewise linear gap cost.BMC Bioinformatics. 2006 Dec 1;7:524. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-7-524. BMC Bioinformatics. 2006. PMID: 17137519 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of Parallel Implementations for the Smith-Waterman Algorithm.Interdiscip Sci. 2022 Mar;14(1):1-14. doi: 10.1007/s12539-021-00473-0. Epub 2021 Sep 6. Interdiscip Sci. 2022. PMID: 34487327 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Finding homologs to nucleic acid or protein sequences using the framesearch program.Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2002 Aug;Chapter 3:Unit 3.2. doi: 10.1002/0471250953.bi0302s00. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2002. PMID: 18792937 Review.
Cited by
-
Fast noisy long read alignment with multi-level parallelism.BMC Bioinformatics. 2025 May 2;26(1):118. doi: 10.1186/s12859-025-06129-w. BMC Bioinformatics. 2025. PMID: 40316905 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the T-cell receptor beta chain repertoire in tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes.Cancer Med. 2016 Sep;5(9):2513-21. doi: 10.1002/cam4.828. Epub 2016 Jul 27. Cancer Med. 2016. PMID: 27465739 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lloyd S, Snell QO. Hardware Accelerated Sequence Alignment with Traceback. International Journal of Reconfigurable Computing. 2009;2009:10. [Article ID 762362]
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

