Chemotherapy-induced cognitive impairment is associated with decreases in cell proliferation and histone modifications
- PMID: 22152030
- PMCID: PMC3252305
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2202-12-124
Chemotherapy-induced cognitive impairment is associated with decreases in cell proliferation and histone modifications
Abstract
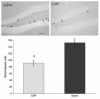
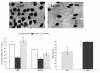
Background: In this study, we examined the effects of cyclophosphamide, methothrexate, and 5-Fluorouracil (CMF) drug combination on various aspects of learning and memory. We also examined the effects of CMF on cell proliferation and chromatin remodeling as possible underlying mechanisms to explain chemotherapy-associated cognitive dysfunction. Twenty-four adult female Wistar rats were included in the study and had minimitter implantation for continuous activity monitoring two weeks before the chemotherapy regimen was started. Once baseline activity data were collected, rats were randomly assigned to receive either CMF or saline injections given intraperitoneally. Treatments were given once a week for a total of 4 weeks. Two weeks after the last injection, rats were tested in the water maze for spatial learning and memory ability as well as discrimination learning. Bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) injection was given at 100 mg/Kg intraperitoneally 4 hours prior to euthanasia to determine hippocampal cell proliferation while histone acetylation and histone deacetylase activity was measured to determine CMF effects on chromatin remodeling.
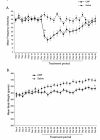
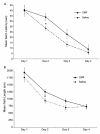
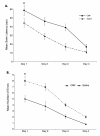
Results: Our data showed learning and memory impairment following CMF administration independent of the drug effects on physical activity. In addition, CMF-treated rats showed decreased hippocampal cell proliferation, associated with increased histone acetylation and decreased histone deacetylase activity.
Conclusions: These results suggest the negative consequences of chemotherapy on brain function and that anti-cancer drugs can adversely affect the self-renewal potential of neural progenitor cells and also chromatin remodeling in the hippocampus. The significance of our findings lie on the possible usefulness of animal models in addressing the clinical phenomenon of 'chemobrain.'
Figures

Similar articles
-
Physical exercise prevents cognitive impairment by enhancing hippocampal neuroplasticity and mitochondrial function in doxorubicin-induced chemobrain.Neuropharmacology. 2018 May 1;133:451-461. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.02.013. Neuropharmacology. 2018. PMID: 29477301
-
Interplay of MeCP2/REST/Synaptophysin-BDNF and intranasal oxytocin influence on Aβ-induced memory and cognitive impairments.Behav Brain Res. 2025 Jan 5;476:115235. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2024.115235. Epub 2024 Sep 3. Behav Brain Res. 2025. PMID: 39236931
-
Impaired cognitive function and hippocampal neurogenesis following cancer chemotherapy.Clin Cancer Res. 2012 Apr 1;18(7):1954-65. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-2000. Epub 2012 Feb 14. Clin Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22338017
-
Chemotherapy, cognitive impairment and hippocampal toxicity.Neuroscience. 2015 Nov 19;309:224-32. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.06.016. Epub 2015 Jun 15. Neuroscience. 2015. PMID: 26086545 Review.
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitors in cancer therapy.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2007 May;16(5):659-78. doi: 10.1517/13543784.16.5.659. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2007. PMID: 17461739 Review.
Cited by
-
Why, After Chemotherapy, is it Necessary to Assess Memory Using Translational Testing?Breast Cancer (Auckl). 2012;6:181-90. doi: 10.4137/BCBCR.S10293. Epub 2012 Nov 19. Breast Cancer (Auckl). 2012. PMID: 23226022 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanosensory encoding dysfunction emerges from cancer-chemotherapy interaction.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Nov 24;9:1017427. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.1017427. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 36504708 Free PMC article.
-
The chemotherapeutic agent paclitaxel selectively impairs learning while sparing source memory and spatial memory.Behav Brain Res. 2017 Mar 1;320:48-57. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2016.11.042. Epub 2016 Nov 28. Behav Brain Res. 2017. PMID: 27908748 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of Chemotherapy-Induced Neurotoxicity.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Mar 28;13:750507. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.750507. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35418856 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemotherapy-Induced Cognitive Impairment and Hippocampal Neurogenesis: A Review of Physiological Mechanisms and Interventions.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 24;22(23):12697. doi: 10.3390/ijms222312697. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34884513 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- van Dam FS, Schagen SB, Muller MJ, Boogerd W, vd Wall E, Droogleever Fortuyn ME, Rodenhuis S. Impairment of cognitive function in women receiving adjuvant treatment for high-risk breast cancer: high-dose versus standard-dose chemotherapy. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1998;90:210–218. doi: 10.1093/jnci/90.3.210. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wieneke MH, Dienst ER. Neuropsychological assessment of cognitive functioning following chemotherapy for breast cancer. Psychooncology. 1995;4:61–66. doi: 10.1002/pon.2960040108. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

