High level expression of Acidothermus cellulolyticus β-1, 4-endoglucanase in transgenic rice enhances the hydrolysis of its straw by cultured cow gastric fluid
- PMID: 22152050
- PMCID: PMC3307496
- DOI: 10.1186/1754-6834-4-58
High level expression of Acidothermus cellulolyticus β-1, 4-endoglucanase in transgenic rice enhances the hydrolysis of its straw by cultured cow gastric fluid
Abstract
Background: Large-scale production of effective cellulose hydrolytic enzymes is the key to the bioconversion of agricultural residues to ethanol. The goal of this study was to develop a rice plant as a bioreactor for the large-scale production of cellulose hydrolytic enzymes via genetic transformation, and to simultaneously improve rice straw as an efficient biomass feedstock for conversion of cellulose to glucose.
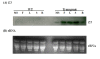
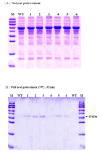
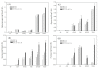
Results: In this study, the cellulose hydrolytic enzyme β-1, 4-endoglucanase (E1) gene, from the thermophilic bacterium Acidothermus cellulolyticus, was overexpressed in rice through Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. The expression of the bacterial E1 gene in rice was driven by the constitutive Mac promoter, a hybrid promoter of Ti plasmid mannopine synthetase promoter and cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter enhancer, with the signal peptide of tobacco pathogenesis-related protein for targeting the E1 protein to the apoplastic compartment for storage. A total of 52 transgenic rice plants from six independent lines expressing the bacterial E1 enzyme were obtained that expressed the gene at high levels without severely impairing plant growth and development. However, some transgenic plants exhibited a shorter stature and flowered earlier than the wild type plants. The E1 specific activities in the leaves of the highest expressing transgenic rice lines were about 20-fold higher than those of various transgenic plants obtained in previous studies and the protein amounts accounted for up to 6.1% of the total leaf soluble protein. A zymogram and temperature-dependent activity analyses demonstrated the thermostability of the E1 enzyme and its substrate specificity against cellulose, and a simple heat treatment can be used to purify the protein. In addition, hydrolysis of transgenic rice straw with cultured cow gastric fluid for one hour at 39°C and another hour at 81°C yielded 43% more reducing sugars than wild type rice straw.
Conclusion: Taken together, these data suggest that transgenic rice can effectively serve as a bioreactor for the large-scale production of active, thermostable cellulose hydrolytic enzymes. As a feedstock, direct expression of large amount of cellulases in transgenic rice may also facilitate saccharification of cellulose in rice straw and significantly reduce the costs for hydrolytic enzymes.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Optimization of Acidothermus cellulolyticus endoglucanase (E1) production in transgenic tobacco plants by transcriptional, post-transcription and post-translational modification.Transgenic Res. 2005 Oct;14(5):627-43. doi: 10.1007/s11248-005-5695-5. Transgenic Res. 2005. PMID: 16245154
-
Enhanced conversion of plant biomass into glucose using transgenic rice-produced endoglucanase for cellulosic ethanol.Transgenic Res. 2007 Dec;16(6):739-49. doi: 10.1007/s11248-006-9064-9. Epub 2007 Jan 20. Transgenic Res. 2007. PMID: 17237981
-
Expression of an Acidothermus cellulolyticus endoglucanase in transgenic rice seeds.Protein Expr Purif. 2012 Apr;82(2):279-83. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2012.01.011. Epub 2012 Jan 28. Protein Expr Purif. 2012. PMID: 22306743
-
Saccharification of rice straw by cellulase from a local Trichoderma harzianum SNRS3 for biobutanol production.BMC Biotechnol. 2014 Dec 12;14:103. doi: 10.1186/s12896-014-0103-y. BMC Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 25496491 Free PMC article.
-
Heterologous Acidothermus cellulolyticus 1,4-beta-endoglucanase E1 produced within the corn biomass converts corn stover into glucose.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2007 Apr;137-140(1-12):207-19. doi: 10.1007/s12010-007-9053-3. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2007. PMID: 18478390
Cited by
-
Multifunctional RNA Binding Protein OsTudor-SN in Storage Protein mRNA Transport and Localization.Plant Physiol. 2017 Dec;175(4):1608-1623. doi: 10.1104/pp.17.01388. Epub 2017 Oct 30. Plant Physiol. 2017. PMID: 29084903 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic engineering of grass cell wall polysaccharides for biorefining.Plant Biotechnol J. 2017 Sep;15(9):1071-1092. doi: 10.1111/pbi.12764. Epub 2017 Jun 30. Plant Biotechnol J. 2017. PMID: 28557198 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thermophilic and alkaliphilic Actinobacteria: biology and potential applications.Front Microbiol. 2015 Sep 25;6:1014. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.01014. eCollection 2015. Front Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26441937 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acidothermus cellulolyticus E1 endoglucanase expressed in planta undergoes extensive hydroxyproline-O-glycosylation and exhibits enhanced impact on biomass digestibility.Plant Cell Rep. 2024 Jul 29;43(8):202. doi: 10.1007/s00299-024-03291-y. Plant Cell Rep. 2024. PMID: 39073636 Free PMC article.
-
Ethanol inducible expression of a mesophilic cellulase avoids adverse effects on plant development.Biotechnol Biofuels. 2013 Apr 16;6(1):53. doi: 10.1186/1754-6834-6-53. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2013. PMID: 23587418 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ward OP, Singh A. Bioethanol technology: developments and perspectives. Adv Appl Microbiol. 2002;51:53–80. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

