Human herpesvirus 6A induces apoptosis of primary human fetal astrocytes via both caspase-dependent and -independent pathways
- PMID: 22152093
- PMCID: PMC3253131
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-422X-8-530
Human herpesvirus 6A induces apoptosis of primary human fetal astrocytes via both caspase-dependent and -independent pathways
Abstract
Background: Human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6) is a T-lymphtropic and neurotropic virus that can infect various types of cells. Sequential studies reported that apoptosis of glia and neurons induced by HHV-6 might act a potential trigger for some central nervous system (CNS) diseases. HHV-6 is involved in the pathogenesis of encephalitis, multiple sclerosis (MS) and fatigue syndrome. However, the mechanisms responsible for the apoptosis of infected CNS cells induced by HHV-6 are poorly understood. In this study, we investigated the cell death processes of primary human fetal astrocytes (PHFAs) during productive HHV-6A infection and the underlying mechanisms.
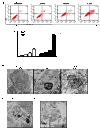
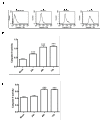
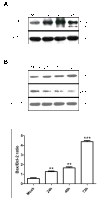
Results: HHV-6A can cause productive infection in primary human fetal astrocytes. Annexin V-PI staining and electron microscopic analysis indicated that HHV-6A was an inducer of apoptosis. The cell death was associated with activation of caspase-3 and cleavage of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP), which is known to be an important substrate for activated caspase-3. Caspase-8 and -9 were also significantly activated in HHV-6A-infected cells. Moreover, HHV-6A infection led to Bax up-regulation and Bcl-2 down-regulation. HHV-6A infection increased the release of Smac/Diablo, AIF and cytochrome c from mitochondria to cytosol, which induced apoptosis via the caspase-dependent and -independent pathways. In addition, we also found that anti-apoptotic factors such as IAPs and NF-κB decreased in HHV-6A infected PHFAs.
Conclusion: This is the first demonstration of caspase-dependent and -independent apoptosis in HHV-6A-infected glial cells. These findings would be helpful in understanding the mechanisms of CNS diseases caused by HHV-6.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Human herpesvirus 6A induces apoptosis of HSB-2 cells via a mitochondrion-related caspase pathway.J Biomed Res. 2010 Nov;24(6):444-51. doi: 10.1016/S1674-8301(10)60059-0. J Biomed Res. 2010. PMID: 23554661 Free PMC article.
-
Coxiella burnetii induces apoptosis during early stage infection via a caspase-independent pathway in human monocytic THP-1 cells.PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e30841. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030841. Epub 2012 Jan 27. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22303462 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of apoptosis by apicidin, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, via the activation of mitochondria-dependent caspase cascades in human Bcr-Abl-positive leukemia cells.Clin Cancer Res. 2003 Oct 15;9(13):5018-27. Clin Cancer Res. 2003. PMID: 14581377
-
The role of herpesvirus 6A and 6B in multiple sclerosis and epilepsy.Scand J Immunol. 2020 Dec;92(6):e12984. doi: 10.1111/sji.12984. Epub 2020 Oct 23. Scand J Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33037649 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Possible role of human herpesvirus 6 as a trigger of autoimmune disease.ScientificWorldJournal. 2013 Oct 24;2013:867389. doi: 10.1155/2013/867389. eCollection 2013. ScientificWorldJournal. 2013. PMID: 24282390 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptome sequencing of neurologic diseases associated genes in HHV-6A infected human astrocyte.Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 26;7(30):48070-48080. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10127. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27344170 Free PMC article.
-
Human herpesvirus type 2 infection of primary murine astrocytes causes disruption of the mitochondrial network and remodeling of the actin cytoskeleton: an in vitro morphological study.Arch Virol. 2021 May;166(5):1371-1383. doi: 10.1007/s00705-021-05025-x. Epub 2021 Mar 14. Arch Virol. 2021. PMID: 33715038 Free PMC article.
-
Incidental Detection of Human Herpesvirus-6 in Cerebrospinal Fluid Analysis: To Treat or Not to Treat?Cureus. 2022 Jun 3;14(6):e25629. doi: 10.7759/cureus.25629. eCollection 2022 Jun. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35785001 Free PMC article.
-
The Interplay between Natural Killer Cells and Human Herpesvirus-6.Viruses. 2017 Dec 1;9(12):367. doi: 10.3390/v9120367. Viruses. 2017. PMID: 29194419 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HHV-6A infection induces amyloid-beta expression and activation of microglial cells.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2019 Dec 12;11(1):104. doi: 10.1186/s13195-019-0552-6. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31831060 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

