Baclofen alters gustatory discrimination capabilities and induces a conditioned taste aversion (CTA)
- PMID: 22152100
- PMCID: PMC3253697
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-0500-4-527
Baclofen alters gustatory discrimination capabilities and induces a conditioned taste aversion (CTA)
Abstract
Background: Studies intending to measure drug-induced changes in learning and memory are challenged to parse out the effects of drugs on sensory, motor, and associative systems in the brain. In the context of conditioned taste aversion (CTA), drugs that alter the sensorium of subjects and affect their ability to taste and/or feel malaise may limit the ability of investigators to make conclusions about associative effects of these substances. Since the GABAergic system is implicated in inhibition, the authors were hopeful to use the GABA agonist, baclofen (BAC), to enhance extinction of a CTA, but first a preliminary evaluation of BAC's peripheral effects on animals' sensorium had to be completed due to a lack of published literature in this area.
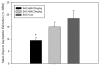
Findings: Our first experiment aimed to evaluate the extent to which the GABAB agonist, BAC, altered the ability of rats to differentiate between 0.3% and 0.6% saccharin (SAC) in a two bottle preference test. Here we report that 2 or 3 mg/kg (i.p.) BAC, but not 1 mg/kg BAC, impaired animals' gustatory discrimination abilities in this task. Furthermore, when SAC consumption was preceded by 2 or 3 mg/kg (i.p.) BAC, rats depressed their subsequent SAC drinking.A second experiment evaluated if the suppression of SAC and water drinking (revealed in Experiment 1) was mediated by amnesiac effects of BAC or whether BAC possessed US properties in the context of the CTA paradigm. The time necessary to reach an asymptotic level of CTA extinction was not significantly different in those animals that received the 3 mg/kg dose of BAC compared to more conventionally SAC + lithium chloride (LiCl, 81 mg/kg) conditioned animals.
Conclusions: Our findings were not consistent with a simple amnesia-of-neophobia explanation. Instead, results indicated that 2 and 3 mg/kg (i.p.) BAC were capable of inducing a CTA, which was extinguishable via repeated presentations of SAC only. Our data indicate that, depending on the dose, BAC can alter SAC taste discrimination and act as a potent US in the context of a CTA paradigm.
Figures
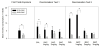

Similar articles
-
Spontaneous recovery of a conditioned taste aversion differentially alters extinction-induced changes in c-Fos protein expression in rat amygdala and neocortex.Brain Res. 2007 Jun 4;1152:139-57. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2007.03.050. Epub 2007 Mar 23. Brain Res. 2007. PMID: 17442279
-
Ketamine blocks a conditioned taste aversion (CTA) in neonatal rats.Physiol Behav. 1998 Jun 1;64(3):381-90. doi: 10.1016/s0031-9384(98)00097-3. Physiol Behav. 1998. PMID: 9748108
-
Chronic dietary magnesium-L-threonate speeds extinction and reduces spontaneous recovery of a conditioned taste aversion.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2013 May;106:16-26. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2013.02.019. Epub 2013 Mar 6. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2013. PMID: 23474371 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in lithium-induced conditioned taste aversion learning.Eur J Pharmacol. 2015 Dec 5;768:182-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.10.052. Epub 2015 Oct 30. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26524411 Review.
-
Electrophysiological Representation of Taste Memory.In: Bermúdez-Rattoni F, editor. Neural Plasticity and Memory: From Genes to Brain Imaging. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2007. Chapter 6. In: Bermúdez-Rattoni F, editor. Neural Plasticity and Memory: From Genes to Brain Imaging. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2007. Chapter 6. PMID: 21204429 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Baclofen administration alters fear extinction and GABAergic protein levels.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2012 Oct;98(3):261-71. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2012.09.005. Epub 2012 Sep 23. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2012. PMID: 23010137 Free PMC article.
-
Baclofen-induced reductions in optional food intake depend upon food composition.Appetite. 2013 May;64:62-70. doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2013.01.002. Epub 2013 Jan 12. Appetite. 2013. PMID: 23321345 Free PMC article.
-
The Insula and Taste Learning.Front Mol Neurosci. 2017 Nov 3;10:335. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2017.00335. eCollection 2017. Front Mol Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 29163022 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Delving into the reducing effects of the GABAB positive allosteric modulator, KK-92A, on alcohol-related behaviors in rats.Alcohol. 2023 Nov;112:61-70. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2023.07.004. Epub 2023 Jul 24. Alcohol. 2023. PMID: 37495087 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

