Volume of the human septal forebrain region is a predictor of source memory accuracy
- PMID: 22152217
- PMCID: PMC3339258
- DOI: 10.1017/S1355617711001421
Volume of the human septal forebrain region is a predictor of source memory accuracy
Abstract
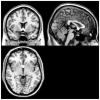
Septal nuclei, components of basal forebrain, are strongly and reciprocally connected with hippocampus, and have been shown in animals to play a critical role in memory. In humans, the septal forebrain has received little attention. To examine the role of human septal forebrain in memory, we acquired high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging scans from 25 healthy subjects and calculated septal forebrain volume using recently developed probabilistic cytoarchitectonic maps. We indexed memory with the California Verbal Learning Test-II. Linear regression showed that bilateral septal forebrain volume was a significant positive predictor of recognition memory accuracy. More specifically, larger septal forebrain volume was associated with the ability to recall item source/context accuracy. Results indicate specific involvement of septal forebrain in human source memory, and recall the need for additional research into the role of septal nuclei in memory and other impairments associated with human diseases.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparison of human septal nuclei MRI measurements using automated segmentation and a new manual protocol based on histology.Neuroimage. 2014 Aug 15;97:245-51. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.04.026. Epub 2014 Apr 13. Neuroimage. 2014. PMID: 24736183 Free PMC article.
-
Association between subcortical volumes and verbal memory in unmedicated depressed patients and healthy controls.Neuropsychologia. 2012 Jul;50(9):2348-55. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2012.06.003. Epub 2012 Jun 17. Neuropsychologia. 2012. PMID: 22714007 Free PMC article.
-
The forebrain medial septal region and nociception.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2017 Feb;138:238-251. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2016.07.017. Epub 2016 Jul 19. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2017. PMID: 27444843 Review.
-
Basal Forebrain Impairment: Understanding the Mnemonic Function of the Septal Region Translates in Therapeutic Advances.Front Neural Circuits. 2022 May 31;16:916499. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2022.916499. eCollection 2022. Front Neural Circuits. 2022. PMID: 35712645 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disassociation of verbal learning and hippocampal volume in type 2 diabetes and major depression.Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2015 Apr;30(4):393-9. doi: 10.1002/gps.4149. Epub 2014 Jun 12. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 24920010 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Evidence for evolutionary specialization in human limbic structures.Front Hum Neurosci. 2014 May 20;8:277. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2014.00277. eCollection 2014. Front Hum Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24904348 Free PMC article.
-
A global view of aging and Alzheimer's pathogenesis-associated cell population dynamics and molecular signatures in human and mouse brains.Nat Genet. 2023 Dec;55(12):2104-2116. doi: 10.1038/s41588-023-01572-y. Epub 2023 Nov 30. Nat Genet. 2023. PMID: 38036784 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of medial septum cholinergic neurons restores cognitive function in temporal lobe epilepsy.Neural Regen Res. 2023 Nov;18(11):2459-2465. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.371369. Neural Regen Res. 2023. PMID: 37282477 Free PMC article.
-
Brain mechanisms underlying the inhibitory control of thought.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2025 Jul;26(7):415-437. doi: 10.1038/s41583-025-00929-y. Epub 2025 May 16. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40379896 Review.
-
Septal nuclei enlargement in human temporal lobe epilepsy without mesial temporal sclerosis.Neurology. 2013 Jan 29;80(5):487-91. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e31827f0ed7. Epub 2013 Jan 9. Neurology. 2013. PMID: 23303846 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexander MP, Freedman M. Amnesia after anterior communicating artery aneurysm rupture. Neurology. 1984;34(6):752–757. - PubMed
-
- Ashburner J. A fast diffeomorphic image registration algorithm. Neuroimage. 2007;38(1):95–113. - PubMed
-
- Caplan JB, McIntosh AR, De Rosa E. Two distinct functional networks for successful resolution of proactive interference. Cerebral Cortex. 2007;17(7):1650–1663. - PubMed
-
- Colom LV, Garrido-Sanabria E. Modulation of normal and altered hippocampal excitability states by septal networks. Journal of Neuroscience Research. 2007;85(13):2839–2843. - PubMed
-
- De Rosa E, Desmond JE, Anderson AK, Pfefferbaum A, Sullivan EV. The human basal forebrain integrates the old and the new. Neuron. 2004;41(5):825–837. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

