Effect of prior medical treatments on ischemic stroke severity and outcome
- PMID: 22152434
- PMCID: PMC3814556
Effect of prior medical treatments on ischemic stroke severity and outcome
Abstract
Antiplatelets, antihypertensives, and statins might reduce the severity of the event or improve outcome in patients who, despite prior medical treatment, have a stroke. We evaluated, in patients who had an ischemic stroke, the effect, on stroke severity and outcome, of prior treatment with antiplatelets, antihypertensives, and statins, used either alone or in a three-drug combination. Stroke in Italy and Related Impact on Outcome (SIRIO) was a prospective, nationwide, multicenter, hospital-based, observational study that included patients aged.18 years with acute ischemic stroke. We studied 2,529 acute ischemic stroke patients from the SIRIO population: 887 were antiplatelet users, 1,497 antihypertensive users, 231 statin users, and 138 three-drug combination users prior to the index event. The adjusted logistic regression analysis showed an association between prior treatment with statins and good functional outcome at discharge, while prior treatment with antiplatelets, antihypertensives or the three-drug combination did not influence severity or outcome. The absolute probability of a good functional outcome was 46.3% (95% CI: 40.3%-53.2%) in statin users and 36.7% (95% CI: 34.7%-38.7%) in non-users of statins; the absolute risk difference was 9.6% (95% CI: 2.9%-16.4%; p=0.004). Prior treatment with antiplatelets, antihypertensives, or the three-drug combination did not influence stroke severity or outcome, while prior treatment with statins did not influence stroke severity but was associated with a better functional outcome.
Figures
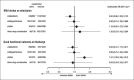
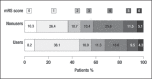
References
-
- Sacco RL , Adams R , Albers G , et al. American Heart Association; American Stroke Association Council on Stroke; Council on Cardiovascular Radiology and Intervention; American Academy of Neurology Guidelines for prevention of stroke in patients with ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack: a statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association Council on Stroke: co-sponsored by the Council on Cardiovascular Radiology and Intervention: the American Academy of Neurology affirms the value of this guideline . Stroke . 2006 ; 37 : 577 – 617 . - PubMed
-
- Alvarez-Sabín J , Huertas R , Quintana M , et al. Prior statin use may be associated with improved stroke outcome after tissue plasminogen activator . Stroke . 2007 ; 38 : 1076 – 1078 . - PubMed
-
- Deplanque D , Masse I , Lefebvre C , Libersa C , Leys D , Bordet R . Prior TIA, lipid-lowering drug use, and physical activity decrease ischemic stroke severity . Neurology . 2006 ; 67 : 1403 – 1410 . - PubMed
-
- Goldstein LB , Amarenco P , Zivin J , et al. Stroke Prevention by Aggressive Reduction in Cholesterol Levels Investigators. Statin treatment and stroke outcome in the Stroke Prevention by Aggressive Reduction in Cholesterol Levels (SPARCL) trial . Stroke . 2009 ; 40 : 3526 – 3531 . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
