In vivo and transcriptome-wide identification of RNA binding protein target sites
- PMID: 22152485
- PMCID: PMC3253457
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.11.009
In vivo and transcriptome-wide identification of RNA binding protein target sites
Abstract
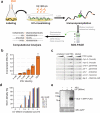
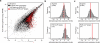
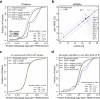
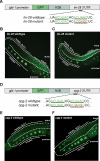
Animal mRNAs are regulated by hundreds of RNA binding proteins (RBPs). The identification of RBP targets is crucial for understanding their function. A recent method, PAR-CLIP, uses photoreactive nucleosides to crosslink RBPs to target RNAs in cells prior to immunoprecipitation. Here, we establish iPAR-CLIP (in vivo PAR-CLIP) to determine, at nucleotide resolution, transcriptome-wide binding sites of GLD-1, a conserved, germline-specific translational repressor in C. elegans. We identified 439 reproducible target mRNAs and demonstrate an excellent dynamic range of target detection by iPAR-CLIP. Upon GLD-1 knockdown, protein but not mRNA expression of the 439 targets was specifically upregulated, demonstrating functionality. Finally, we discovered strongly conserved GLD-1 binding sites near the start codon of target genes. These sites are functional in vitro and likely confer strong repression in vivo. We propose that GLD-1 interacts with the translation machinery near the start codon, a so-far-unknown mode of gene regulation in eukaryotes.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Modeling the binding specificity of the RNA-binding protein GLD-1 suggests a function of coding region-located sites in translational repression.RNA. 2013 Oct;19(10):1317-26. doi: 10.1261/rna.037531.112. Epub 2013 Aug 23. RNA. 2013. PMID: 23974436 Free PMC article.
-
Translation repression by GLD-1 protects its mRNA targets from nonsense-mediated mRNA decay in C. elegans.Genes Dev. 2004 May 1;18(9):1047-59. doi: 10.1101/gad.1188404. Epub 2004 Apr 22. Genes Dev. 2004. PMID: 15105376 Free PMC article.
-
PAR-CliP--a method to identify transcriptome-wide the binding sites of RNA binding proteins.J Vis Exp. 2010 Jul 2;(41):2034. doi: 10.3791/2034. J Vis Exp. 2010. PMID: 20644507 Free PMC article.
-
C. elegans star proteins, GLD-1 and ASD-2, regulate specific RNA targets to control development.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010;693:106-22. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-7005-3_8. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010. PMID: 21189689 Review.
-
RNA-binding proteins.WormBook. 2006 Apr 18:1-13. doi: 10.1895/wormbook.1.79.1. WormBook. 2006. PMID: 18050487 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Understanding the binding specificities of mRNA targets by the mammalian Quaking protein.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Nov 18;47(20):10564-10579. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz877. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 31602485 Free PMC article.
-
CapR: revealing structural specificities of RNA-binding protein target recognition using CLIP-seq data.Genome Biol. 2014 Jan 21;15(1):R16. doi: 10.1186/gb-2014-15-1-r16. Genome Biol. 2014. PMID: 24447569 Free PMC article.
-
HITS-CLIP reveals sex-differential RNA binding and alterative splicing regulation of SRm160 in Drosophila.J Mol Cell Biol. 2019 Feb 1;11(2):170-181. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjy029. J Mol Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 29750417 Free PMC article.
-
C. elegans RNA-binding protein GLD-1 recognizes its multiple targets using sequence, context, and structural information to repress translation.Worm. 2013 Oct 1;2(4):e26548. doi: 10.4161/worm.26548. Worm. 2013. PMID: 24744981 Free PMC article.
-
Competence for chemical reprogramming of sexual fate correlates with an intersexual molecular signature in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genetics. 2014 Oct;198(2):561-75. doi: 10.1534/genetics.114.169409. Epub 2014 Aug 21. Genetics. 2014. PMID: 25146970 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bailey TL, Elkan C. Fitting a mixture model by expectation maximization to discover motifs in biopolymers. Proceedings / … International Conference on Intelligent Systems for Molecular Biology; ISMB.1994. pp. 28–36. - PubMed
-
- Beanan MJ, Strome S. Characterization of a germ-line proliferation mutation in C. elegans. Development (Cambridge, England) 1992;116:755–766. - PubMed
-
- Cox J, Mann M. MaxQuant enables high peptide identification rates, individualized p.p.b.-range mass accuracies and proteome-wide protein quantification. Nature biotechnology. 2008;26:1367–1372. - PubMed
-
- Didiano D, Hobert O. Perfect seed pairing is not a generally reliable predictor for miRNA-target interactions. Nature structural & molecular biology. 2006;13:849–851. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

