Lipoic acid synthetase deficiency causes neonatal-onset epilepsy, defective mitochondrial energy metabolism, and glycine elevation
- PMID: 22152680
- PMCID: PMC3234378
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.11.011
Lipoic acid synthetase deficiency causes neonatal-onset epilepsy, defective mitochondrial energy metabolism, and glycine elevation
Abstract
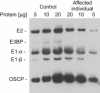
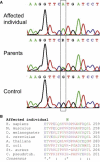
Lipoic acid is an essential prosthetic group of four mitochondrial enzymes involved in the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate, α-ketoglutarate, and branched chain amino acids and in the glycine cleavage. Lipoic acid is synthesized stepwise within mitochondria through a process that includes lipoic acid synthetase. We identified the homozygous mutation c.746G>A (p.Arg249His) in LIAS in an individual with neonatal-onset epilepsy, muscular hypotonia, lactic acidosis, and elevated glycine concentration in plasma and urine. Investigation of the mitochondrial energy metabolism showed reduced oxidation of pyruvate and decreased pyruvate dehydrogenase complex activity. A pronounced reduction of the prosthetic group lipoamide was found in lipoylated proteins.
Copyright © 2011 The American Society of Human Genetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Hiltunen J.K., Autio K.J., Schonauer M.S., Kursu V.A., Dieckmann C.L., Kastaniotis A.J. Mitochondrial fatty acid synthesis and respiration. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2010;1797:1195–1202. - PubMed
-
- Jilka J.M., Rahmatullah M., Kazemi M., Roche T.E. Properties of a newly characterized protein of the bovine kidney pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. J. Biol. Chem. 1986;261:1858–1867. - PubMed
-
- Morris T.W., Reed K.E., Cronan J.E., Jr. Identification of the gene encoding lipoate-protein ligase A of Escherichia coli. Molecular cloning and characterization of the lplA gene and gene product. J. Biol. Chem. 1994;269:16091–16100. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

