The STARD9/Kif16a kinesin associates with mitotic microtubules and regulates spindle pole assembly
- PMID: 22153075
- PMCID: PMC4180425
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.11.020
The STARD9/Kif16a kinesin associates with mitotic microtubules and regulates spindle pole assembly
Abstract
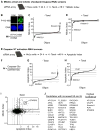
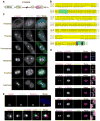
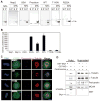
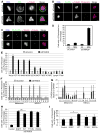
During cell division, cells form the microtubule-based mitotic spindle, a highly specialized and dynamic structure that mediates proper chromosome transmission to daughter cells. Cancer cells can show perturbed mitotic spindles and an approach in cancer treatment has been to trigger cell killing by targeting microtubule dynamics or spindle assembly. To identify and characterize proteins necessary for spindle assembly, and potential antimitotic targets, we performed a proteomic and genetic analysis of 592 mitotic microtubule copurifying proteins (MMCPs). Screening for regulators that affect both mitosis and apoptosis, we report the identification and characterization of STARD9, a kinesin-3 family member, which localizes to centrosomes and stabilizes the pericentriolar material (PCM). STARD9-depleted cells have fragmented PCM, form multipolar spindles, activate the spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC), arrest in mitosis, and undergo apoptosis. Interestingly, STARD9-depletion synergizes with the chemotherapeutic agent taxol to increase mitotic death, demonstrating that STARD9 is a mitotic kinesin and a potential antimitotic target.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A centrosomal protein STARD9 promotes microtubule stability and regulates spindle microtubule dynamics.Cell Cycle. 2018;17(16):2052-2068. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2018.1513764. Epub 2018 Sep 11. Cell Cycle. 2018. PMID: 30160609 Free PMC article.
-
STARD9/Kif16a is a novel mitotic kinesin and antimitotic target.Bioarchitecture. 2012 Jan 1;2(1):19-22. doi: 10.4161/bioa.19766. Bioarchitecture. 2012. PMID: 22754624 Free PMC article.
-
A novel genetic syndrome with STARD9 mutation and abnormal spindle morphology.Am J Med Genet A. 2017 Oct;173(10):2690-2696. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.38391. Epub 2017 Aug 4. Am J Med Genet A. 2017. PMID: 28777490
-
Centriole inheritance.Prion. 2008 Jan-Mar;2(1):9-16. doi: 10.4161/pri.2.1.5064. Epub 2008 Jan 12. Prion. 2008. PMID: 19164929 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitotic centromere-associated kinesin (MCAK): a potential cancer drug target.Oncotarget. 2011 Dec;2(12):935-47. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.416. Oncotarget. 2011. PMID: 22249213 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Run length distribution of dimerized kinesin-3 molecular motors: comparison with dimeric kinesin-1.Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 18;9(1):16973. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-53550-2. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31740721 Free PMC article.
-
Multimodal effects of small molecule ROCK and LIMK inhibitors on mitosis, and their implication as anti-leukemia agents.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 18;9(3):e92402. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0092402. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24642638 Free PMC article.
-
A microtubule-associated zinc finger protein, BuGZ, regulates mitotic chromosome alignment by ensuring Bub3 stability and kinetochore targeting.Dev Cell. 2014 Feb 10;28(3):268-81. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2013.12.013. Epub 2014 Jan 23. Dev Cell. 2014. PMID: 24462186 Free PMC article.
-
Functional screening identifies kinesin spindle protein inhibitor filanesib as a potential treatment option for hepatoblastoma.NPJ Precis Oncol. 2025 Apr 25;9(1):122. doi: 10.1038/s41698-025-00915-8. NPJ Precis Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40281281 Free PMC article.
-
Anastral Spindle 3/Rotatin Stabilizes Sol narae and Promotes Cell Survival in Drosophila melanogaster.Mol Cells. 2021 Jan 31;44(1):13-25. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2020.0244. Mol Cells. 2021. PMID: 33510049 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abal M, Keryer G, Bornens M. Centrioles resist forces applied on centrosomes during G2/M transition. Biol Cell. 2005;97:425–434. - PubMed
-
- Alpy F, Tomasetto C. Give lipids a START: the StAR-related lipid transfer (START) domain in mammals. J Cell Sci. 2005;118:2791–2801. - PubMed
-
- Blangy A, Chaussepied P, Nigg EA. Rigor-type mutation in the kinesin-related protein HsEg5 changes its subcellular localization and induces microtubule bundling. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1998;40:174–182. - PubMed
-
- Carter SL, Eklund AC, Kohane IS, Harris LN, Szallasi Z. A signature of chromosomal instability inferred from gene expression profiles predicts clinical outcome in multiple human cancers. Nat Genet. 2006;38:1043–1048. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

