Multisite EPR oximetry from multiple quadrature harmonics
- PMID: 22154283
- PMCID: PMC3257390
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmr.2011.10.016
Multisite EPR oximetry from multiple quadrature harmonics
Abstract
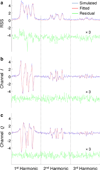
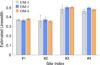
Multisite continuous wave (CW) electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) oximetry using multiple quadrature field modulation harmonics is presented. First, a recently developed digital receiver is used to extract multiple harmonics of field modulated projection data. Second, a forward model is presented that relates the projection data to unknown parameters, including linewidth at each site. Third, a maximum likelihood estimator of unknown parameters is reported using an iterative algorithm capable of jointly processing multiple quadrature harmonics. The data modeling and processing are applicable for parametric lineshapes under nonsaturating conditions. Joint processing of multiple harmonics leads to 2-3-fold acceleration of EPR data acquisition. For demonstration in two spatial dimensions, both simulations and phantom studies on an L-band system are reported.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





References
-
- Kulkarni A, Kuppusamy P, Parinandi N. Oxygen, the lead actor in the pathophysiologic drama: enactment of the trinity of normoxia, hypoxia, and hyperoxia in disease and therapy. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2007;9:1717–1730. - PubMed
-
- Hopf H, Gibson J, Angeles A, Constant J, Feng J, Rollins M, Hussain MZ, Hunt T. Hyperoxia and angiogenesis. Wound Repair Regen. 2005;13:558–564. - PubMed
-
- Gallez B, Mder K, Swartz H. Noninvasive measurement of the pH inside the gut by using pH-sensitive nitroxides. An in vivo EPR study. Magn. Reson. Med. 1996;36:694–697. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

