Formation of P450 · P450 complexes and their effect on P450 function
- PMID: 22155419
- PMCID: PMC3272114
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2011.11.009
Formation of P450 · P450 complexes and their effect on P450 function
Abstract
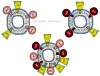
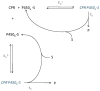
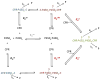
Cytochromes P450 (P450) are membrane-bound enzymes that catalyze the monooxygenation of a diverse array of xenobiotic and endogenous compounds. The P450s responsible for foreign compound metabolism generally are localized in the endoplasmic reticulum of the liver, lung and small intestine. P450 enzymes do not act alone but require an interaction with other electron transfer proteins such as NADPH-cytochrome P450 reductase (CPR) and cytochrome b(5). Because P450s are localized in the endoplasmic reticulum with these and other ER-resident proteins, there is a potential for protein-protein interactions to influence P450 function. There has been increasing evidence that P450 enzymes form complexes in the ER, with compelling support that formation of P450 · P450 complexes can significantly influence their function. Our goal is to review the research supporting the formation of P450 · P450 complexes, their specificity, and how drug metabolism may be affected. This review describes the potential mechanisms by which P450s may interact, and provides evidence to support each of the possible mechanisms. Additionally, evidence for the formation of both heteromeric and homomeric P450 complexes are reviewed. Finally, direct physical evidence for P450 complex formation in solution and in membranes is summarized, and questions directing the future research of functional P450 interactions are discussed with respect to their potential impact on drug metabolism.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Alston K, Robinson RC, Park SS, Gelboin HV, Friedman FK. Interactions among cytochromes P-450 in the endoplasmic reticulum. Detection of chemically cross-linked complexes with monoclonal antibodies. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1991;266:735–739. - PubMed
-
- Backes WL, Batie CJ, Cawley GF. Interactions among P450 enzymes when combined in reconstituted systems: formation of a 2B4-1A2 complex with a high affinity for NADPH-cytochrome P450 reductase. Biochemistry. 1998;37:12852–12859. - PubMed
-
- Backes WL, Eyer CS. Cytochrome P-450 LM2 reduction. Substrate effects on the rate of reductase-LM2 association. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1989;264:6252–6259. - PubMed
-
- Baskin LS, Yang CS. Cross-linking studies of cytochrome P-450 and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-cytochrome P-450 reductase. Biochemistry. 1980;19:2260–2264. - PubMed
-
- Causey KM, Eyer CS, Backes WL. Dual role of phospholipid in the reconstitution of cytochrome P- 450 LM2-dependent activities. Molecular Pharmacology. 1990;38:134–142. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

