Select microRNAs are essential for early development in the sea urchin
- PMID: 22155525
- PMCID: PMC3254792
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2011.11.015
Select microRNAs are essential for early development in the sea urchin
Abstract
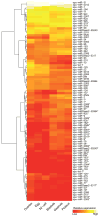
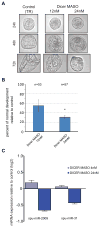
microRNAs (miRNAs) are small noncoding RNAs that mediate post-transcriptional gene regulation and have emerged as essential regulators of many developmental events. The transcriptional network during early embryogenesis of the purple sea urchin, Strongylocentrotus purpuratus, is well described and can serve as an excellent model to test functional contributions of miRNAs in embryogenesis. We examined the loss of function phenotypes of major components of the miRNA biogenesis pathway. Inhibition of de novo synthesis of Drosha and Dicer in the embryo led to consistent developmental defects, a failure to gastrulate, and embryonic lethality, including changes in the steady state levels of transcription factors and signaling molecules involved in germ layer specification. We annotated and profiled small RNA expression from the ovary and several early embryonic stages by deep sequencing followed by computational analysis. miRNAs as well as a large population of putative piRNAs (piwi-interacting RNAs) had dynamic accumulation profiles through early development. Defects in morphogenesis caused by loss of Drosha could be rescued with four miRNAs. Taken together our results indicate that post-transcriptional gene regulation directed by miRNAs is functionally important for early embryogenesis and is an integral part of the early embryonic gene regulatory network in S. purpuratus.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
microRNA-31 regulates skeletogenesis by direct suppression of Eve and Wnt1.Dev Biol. 2021 Apr;472:98-114. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2021.01.008. Epub 2021 Jan 20. Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33484703 Free PMC article.
-
Genes involved in the RNA interference pathway are differentially expressed during sea urchin development.Dev Dyn. 2007 Nov;236(11):3180-90. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.21353. Dev Dyn. 2007. PMID: 17948309
-
MicroRNA-dependent roles of Drosha and Pasha in the Drosophila larval ovary morphogenesis.Dev Biol. 2016 Aug 15;416(2):312-23. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2016.06.026. Epub 2016 Jun 20. Dev Biol. 2016. PMID: 27339292
-
Piecing together the mosaic of early mammalian development through microRNAs.J Biol Chem. 2008 Apr 11;283(15):9505-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R800002200. Epub 2008 Feb 13. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18272516 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA function and mechanism: insights from zebra fish.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006;71:195-203. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2006.71.055. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006. PMID: 17381297 Review.
Cited by
-
Germ Line Versus Soma in the Transition from Egg to Embryo.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2015;113:149-90. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2015.06.003. Epub 2015 Aug 19. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 26358873 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamic Evolution of Repetitive Elements and Chromatin States in Apis mellifera Subspecies.Genes (Basel). 2024 Jan 11;15(1):89. doi: 10.3390/genes15010089. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38254978 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) signaling during gastrulation negatively modulates the abundance of microRNAs that regulate proteins required for cell migration and embryo patterning.J Biol Chem. 2012 Nov 9;287(46):38505-14. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.400598. Epub 2012 Sep 20. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22995917 Free PMC article.
-
microRNA-124 regulates Notch and NeuroD1 to mediate transition states of neuronal development.Dev Neurobiol. 2023 Jan;83(1-2):3-27. doi: 10.1002/dneu.22902. Epub 2022 Nov 23. Dev Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 36336988 Free PMC article.
-
Pattern of Repetitive Element Transcription Segregate Cell Lineages during the Embryogenesis of Sea Urchin Strongylocentrotus purpuratus.Biomedicines. 2021 Nov 21;9(11):1736. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9111736. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34829966 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aravin A, Gaidatzis D, Pfeffer S, Lagos-Quintana M, Landgraf P, Iovino N, Morris P, Brownstein MJ, Kuramochi-Miyagawa S, Nakano T, Chien M, Russo JJ, Ju J, Sheridan R, Sander C, Zavolan M, Tuschl T. A novel class of small RNAs bind to MILI protein in mouse testes. Nature. 2006;442:203–207. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

