Evaluating the genotoxicity of topoisomerase-targeted antibiotics
- PMID: 22155972
- PMCID: PMC3331794
- DOI: 10.1093/mutage/ger089
Evaluating the genotoxicity of topoisomerase-targeted antibiotics
Abstract
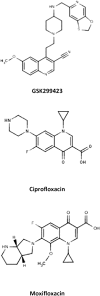
Antibiotics like fluoroquinolones (FQs) that target bacterial type II topoisomerases pose a potential genotoxic risk due to interactions with mammalian topoisomerase II (TOPO II) counterparts. Inhibition of TOPO II can lead to the generation of clastogenic DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) that can in turn manifest in mutagenesis. Thus, methods that allow early identification of drugs that present the greatest hazard are warranted. A rapid, medium-throughput and predictive genotoxicity screen that can be applied to bacterial type II topoisomerase inhibitors is described herein. Maximal induction of the DSB biomarker serine139-phosphorylated histone H2AX (γH2AX) in L5178Y cells was quantified via flow cytometry and correlated with data derived from the mouse lymphoma screen (MLS), a default assay used to rank genotoxic potential. When applied to a class of novel bacterial type II topoisomerase inhibitors (NBTIs) in lead-optimisation, maximal γH2AX induction >1.4-fold (relative to controls) identified 22/27 NBTIs that induced >6-fold relative mutation frequency (MF) in MLS. Moreover, response signatures comprising of γH2AX induction and G(2)M cell cycle arrest elucidated using this approach suggested that these NBTIs, primarily of the H class, operated via a TOPO II poison-like mechanism of action (MoA) similar to FQs. NBTIs that induced ≤6-fold relative MF, which were mainly A class-derived, had less impact on γH2AX (≤1.4-fold) and also evoked G(1) arrest, indicating that their cytotoxic effects were likely mediated through a non-poison MoA. Concordance between assays was 86% (54/63) when 1.4- and 6-fold 'cut offs' were applied. These findings were corroborated through inspection of human TOPO IIα IC(50) data as NBTIs exhibiting equivalent inhibitory capacities had differing genotoxic potencies. Deployed in an early screening capacity, the γH2AX by flow assay coupled with structure-activity relationship evaluation can provide insight into MoA and impact medicinal chemistry efforts, ultimately leading to the production of inherently safer molecules.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Genotoxicity of topoisomerase II inhibitors: an anti-infective perspective.Toxicology. 2008 Dec 30;254(3):192-8. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2008.08.023. Epub 2008 Sep 18. Toxicology. 2008. PMID: 18840496 Review.
-
Emodin triggers DNA double-strand breaks by stabilizing topoisomerase II-DNA cleavage complexes and by inhibiting ATP hydrolysis of topoisomerase II.Toxicol Sci. 2010 Dec;118(2):435-43. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfq282. Epub 2010 Sep 20. Toxicol Sci. 2010. PMID: 20855424
-
Assessment of DNA double-strand breaks and gammaH2AX induced by the topoisomerase II poisons etoposide and mitoxantrone.Mutat Res. 2008 May 10;641(1-2):43-7. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2008.03.005. Epub 2008 Mar 25. Mutat Res. 2008. PMID: 18423498 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship of cellular topoisomerase IIα inhibition to cytotoxicity and published genotoxicity of fluoroquinolone antibiotics in V79 cells.Chem Biol Interact. 2013 Apr 25;203(2):386-90. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2013.01.003. Epub 2013 Jan 20. Chem Biol Interact. 2013. PMID: 23340199
-
International Commission for Protection Against Environmental Mutagens and Carcinogens. Mutagenicity and carcinogenicity of topoisomerase-interactive agents.Mutat Res. 1994 Aug 1;309(1):109-42. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(94)90048-5. Mutat Res. 1994. PMID: 7519727 Review.
Cited by
-
Cellular Pharmacokinetics and Intracellular Activity of Gepotidacin against Staphylococcus aureus Isolates with Different Resistance Phenotypes in Models of Cultured Phagocytic Cells.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018 Mar 27;62(4):e02245-17. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02245-17. Print 2018 Apr. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018. PMID: 29358297 Free PMC article.
-
DNA damage signaling assessed in individual cells in relation to the cell cycle phase and induction of apoptosis.Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2012 Sep-Dec;49(5-6):199-217. doi: 10.3109/10408363.2012.738808. Epub 2012 Nov 9. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2012. PMID: 23137030 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Twist and Turn-Topoisomerase Functions in Mitochondrial DNA Maintenance.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Apr 25;20(8):2041. doi: 10.3390/ijms20082041. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31027213 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advantages of evaluating γH2AX induction in non-clinical drug development.Genes Environ. 2018 May 14;40:10. doi: 10.1186/s41021-018-0098-z. eCollection 2018. Genes Environ. 2018. PMID: 29785231 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selective toxicity of antibacterial agents-still a valid concept or do we miss chances and ignore risks?Infection. 2021 Feb;49(1):29-56. doi: 10.1007/s15010-020-01536-y. Epub 2020 Dec 23. Infection. 2021. PMID: 33367978 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Payne DJ, Gwynn MN, Holmes DJ, Pompliano DL. Drugs for bad bugs: confronting the challenges of antibacterial discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2007;6:29–40. - PubMed
-
- Tse-Dinh YC. Exploring DNA topoisomerases as targets of novel therapeutic agents in the treatment of infectious diseases. Infect. Disord. Drug Targets. 2007;7:3–9. - PubMed
-
- Maxwell A. DNA gyrase as a drug target. Trends Microbiol. 1997;5:102–109. - PubMed
-
- Bradbury BJ, Pucci MJ. Recent advances in bacterial topoisomerase inhibitors. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2008;8:574–581. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

