SOX after SOX: SOXession regulates neurogenesis
- PMID: 22156204
- PMCID: PMC3243053
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.181487.111
SOX after SOX: SOXession regulates neurogenesis
Abstract
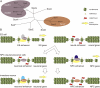
Vertebrate embryonic stem (ES) cells give rise to many different cell types in multistep processes. These involve the establishment of a competent state, specification, differentiation, and maturation, and often involve Sox transcription factors. In this issue of Genes & Development, Bergsland and colleagues (pp. 2453-2464) determine the genome-wide binding profile of Sox2, Sox3, and Sox11 as ES cells become specified to neural precursors and differentiate into neurons. An ordered, sequential binding of these Sox proteins to a common set of gene enhancers was found to drive neurogenesis, as Sox proteins first help to preselect neural genes in ES cells and later ensure their proper activation in neural precursors or neurons.
Figures
Comment on
-
Sequentially acting Sox transcription factors in neural lineage development.Genes Dev. 2011 Dec 1;25(23):2453-64. doi: 10.1101/gad.176008.111. Epub 2011 Nov 15. Genes Dev. 2011. PMID: 22085726 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bani-Yaghoub M, Tremblay RG, Lei JX, Zhang D, Zurakowski B, Sandhu JK, Smith B, Ribecco-Lutkiewicz M, Kennedy J, Walker PR, et al. 2006. Role of Sox2 in the development of the mouse neocortex. Dev Biol 295: 52–66 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
