Global DNA hypomethylation coupled to repressive chromatin domain formation and gene silencing in breast cancer
- PMID: 22156296
- PMCID: PMC3266032
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.125872.111
Global DNA hypomethylation coupled to repressive chromatin domain formation and gene silencing in breast cancer
Abstract
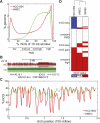
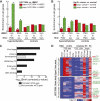
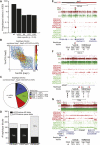
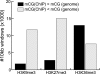
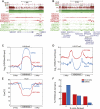
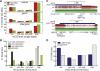
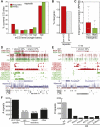
While genetic mutation is a hallmark of cancer, many cancers also acquire epigenetic alterations during tumorigenesis including aberrant DNA hypermethylation of tumor suppressors, as well as changes in chromatin modifications as caused by genetic mutations of the chromatin-modifying machinery. However, the extent of epigenetic alterations in cancer cells has not been fully characterized. Here, we describe complete methylome maps at single nucleotide resolution of a low-passage breast cancer cell line and primary human mammary epithelial cells. We find widespread DNA hypomethylation in the cancer cell, primarily at partially methylated domains (PMDs) in normal breast cells. Unexpectedly, genes within these regions are largely silenced in cancer cells. The loss of DNA methylation in these regions is accompanied by formation of repressive chromatin, with a significant fraction displaying allelic DNA methylation where one allele is DNA methylated while the other allele is occupied by histone modifications H3K9me3 or H3K27me3. Our results show a mutually exclusive relationship between DNA methylation and H3K9me3 or H3K27me3. These results suggest that global DNA hypomethylation in breast cancer is tightly linked to the formation of repressive chromatin domains and gene silencing, thus identifying a potential epigenetic pathway for gene regulation in cancer cells.
Figures

References
-
- Aran D, Toperoff G, Rosenberg M, Hellman A 2011. Replication timing-related and gene body-specific methylation of active human genes. Hum Mol Genet 20: 670–680 - PubMed
-
- Bansal V, Bafna V 2008. HapCUT: An efficient and accurate algorithm for the haplotype assembly problem. Bioinformatics 24: i153–i159 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
