Natural killer cells regulate murine cytomegalovirus-induced sialadenitis and salivary gland disease
- PMID: 22156514
- PMCID: PMC3302420
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.06898-11
Natural killer cells regulate murine cytomegalovirus-induced sialadenitis and salivary gland disease
Abstract
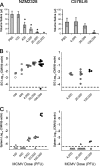
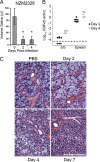
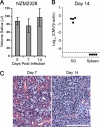
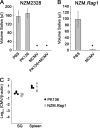
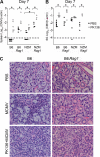
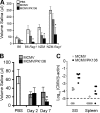
The transmission of herpesviruses depends on viral shedding at mucosal surfaces. The salivary gland represents a major site of persistent viral replication for many viruses, including cytomegalovirus. We established a mouse model of salivary gland dysfunction after acute viral infection and investigated the cellular requirements for the loss of secretion. Murine cytomegalovirus (MCMV) infection severely impaired saliva secretion independently of salivary gland virus levels. Lymphocytes or circulating monocytes/macrophages were not required for secretory dysfunction. Dysfunction occurred before glandular inflammation, suggesting that a soluble mediator initiated the disruption of acinar cell function. Despite genetic differences in innate resistance to MCMV, NK cells protected the host against acinar atrophy and the loss of secretions under conditions of an exceedingly low virus inoculum. NK cells also modulated the type of glandular inflammation after infection, as they prevented an influx of Siglec-F(+) polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs). Therefore, beyond their recognized role in controlling MCMV replication, NK cells preserve organ integrity and function and regulate the innate inflammatory response within the gland.
Figures
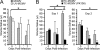

References
-
- Basu D, Williams FM, Ahn CW, Reveille JD. 2006. Changing spectrum of the diffuse infiltrative lymphocytosis syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 55:466–472 - PubMed
-
- Brown MG, et al. 2001. Vital involvement of a natural killer cell activation receptor in resistance to viral infection. Science 292:934–937 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

