Selection and accumulation of an HIV-1 escape mutant by three types of HIV-1-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes recognizing wild-type and/or escape mutant epitopes
- PMID: 22156528
- PMCID: PMC3302409
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.06470-11
Selection and accumulation of an HIV-1 escape mutant by three types of HIV-1-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes recognizing wild-type and/or escape mutant epitopes
Abstract
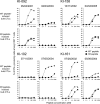
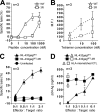
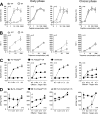
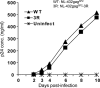
It is known that cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) recognizing HIV-1 escape mutants are elicited in HIV-1-infected individuals, but their role in the control of HIV-1 replication remains unclear. We investigated the antiviral ability of CTLs recognizing the HLA-A*24:02-restricted Gag28 -36 (KYKLKHIVW) epitope and/or its escape mutant (KYRLKHIVW) elicited in the early and chronic phases of the infection. Wild-type (WT)-epitope-specific CTLs, as well as cross-reactive CTLs recognizing both WT and K30R (3R) epitopes, which were predominantly elicited at early and/or chronic phases in HLA-A*24:02(+) individuals infected with the WT virus, suppressed the replication of the WT virus but failed to suppress that of the 3R virus, indicating that the 3R virus was selected by these 2 types of CTLs. On the other hand, cross-reactive and 3R-specific CTLs, which were elicited in those infected with the 3R virus, did not suppress the replication of either WT or 3R virus, indicating that these CTLs did not contribute to the control of 3R virus replication. High accumulation of the 3R mutation was found in a Japanese population recently recruited. The selection and accumulation of this 3R mutation resulted from the antiviral ability of these Gag28-specific CTLs and high prevalence of HLA-A*24:02 in a Japanese population. The present study highlighted the mechanisms for the roles of cross-reactive and mutant-epitope-specific CTLs, as well as high accumulation of escape mutants, in an HIV-1-infected population.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Escape mutation selected by Gag28-36-specific cytotoxic T cells in HLA-A*2402-positive HIV-1-infected donors.Microbes Infect. 2009 Feb;11(2):198-204. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2008.11.005. Epub 2008 Nov 24. Microbes Infect. 2009. PMID: 19063987
-
Different abilities of escape mutant-specific cytotoxic T cells to suppress replication of escape mutant and wild-type human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in new hosts.J Virol. 2008 Jan;82(1):138-47. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01452-07. Epub 2007 Oct 24. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 17959671 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct HIV-1 escape patterns selected by cytotoxic T cells with identical epitope specificity.J Virol. 2013 Feb;87(4):2253-63. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02572-12. Epub 2012 Dec 12. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23236061 Free PMC article.
-
[Control of HIV infection and selection/ accumulation of HIV escape mutants by HIV-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs)].Uirusu. 2013;63(2):209-18. doi: 10.2222/jsv.63.209. Uirusu. 2013. PMID: 25366055 Review. Japanese.
-
[[Research Progress in Escape Mutations of the Human Immunodeficiency Virus under Pressure of HLA-Restricted Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes].Bing Du Xue Bao. 2015 May;31(3):299-306. Bing Du Xue Bao. 2015. PMID: 26470538 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
CD8+ T cells control SIV infection using both cytolytic effects and non-cytolytic suppression of virus production.Nat Commun. 2023 Oct 20;14(1):6657. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-42435-8. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37863982 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Difference in Consensus Sequence between HIV-1 Subtype A/E and Subtype B Viruses on Elicitation of Gag-Specific CD8+ T Cells and Accumulation of HLA-Associated Escape Mutations.J Virol. 2021 Feb 24;95(6):e02061-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02061-20. Print 2021 Feb 24. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 33361435 Free PMC article.
-
Dual HLA B*42 and B*81-reactive T cell receptors recognize more diverse HIV-1 Gag escape variants.Nat Commun. 2018 Nov 27;9(1):5023. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07209-7. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30479346 Free PMC article.
-
Immunogenetics of small ruminant lentiviral infections.Viruses. 2014 Aug 22;6(8):3311-33. doi: 10.3390/v6083311. Viruses. 2014. PMID: 25153344 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effective Suppression of HIV-1 Replication by Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes Specific for Pol Epitopes in Conserved Mosaic Vaccine Immunogens.J Virol. 2019 Mar 21;93(7):e02142-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02142-18. Print 2019 Apr 1. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30674626 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altman JD, et al. 1996. Phenotypic analysis of antigen-specific T lymphocytes. Science 274:94–96 - PubMed
-
- Borrow P, et al. 1997. Antiviral pressure exerted by HIV-1-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) during primary infection demonstrated by rapid selection of CTL escape virus. Nat. Med. 3:205–211 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

