Production of infectious chimeric hepatitis C virus genotype 2b harboring minimal regions of JFH-1
- PMID: 22156532
- PMCID: PMC3302416
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.05386-11
Production of infectious chimeric hepatitis C virus genotype 2b harboring minimal regions of JFH-1
Abstract
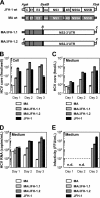
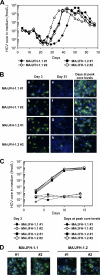
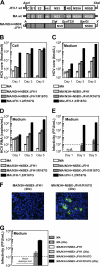
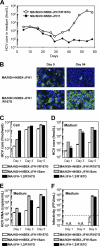
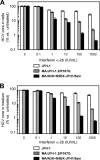
To establish a cell culture system for chimeric hepatitis C virus (HCV) genotype 2b, we prepared a chimeric construct harboring the 5' untranslated region (UTR) to the E2 region of the MA strain (genotype 2b) and the region of p7 to the 3' UTR of the JFH-1 strain (genotype 2a). This chimeric RNA (MA/JFH-1.1) replicated and produced infectious virus in Huh7.5.1 cells. Replacement of the 5' UTR of this chimera with that from JFH-1 (MA/JFH-1.2) enhanced virus production, but infectivity remained low. In a long-term follow-up study, we identified a cell culture-adaptive mutation in the core region (R167G) and found that it enhanced virus assembly. We previously reported that the NS3 helicase (N3H) and the region of NS5B to 3' X (N5BX) of JFH-1 enabled replication of the J6CF strain (genotype 2a), which could not replicate in cells. To reduce JFH-1 content in MA/JFH-1.2, we produced a chimeric viral genome for MA harboring the N3H and N5BX regions of JFH-1, combined with a JFH-1 5' UTR replacement and the R167G mutation (MA/N3H+N5BX-JFH1/R167G). This chimeric RNA replicated efficiently, but virus production was low. After the introduction of four additional cell culture-adaptive mutations, MA/N3H+N5BX-JFH1/5am produced infectious virus efficiently. Using this chimeric virus harboring minimal regions of JFH-1, we analyzed interferon sensitivity and found that this chimeric virus was more sensitive to interferon than JFH-1 and another chimeric virus containing more regions from JFH-1 (MA/JFH-1.2/R167G). In conclusion, we established an HCV genotype 2b cell culture system using a chimeric genome harboring minimal regions of JFH-1. This cell culture system may be useful for characterizing genotype 2b viruses and developing antiviral strategies.
Figures
References
-
- Bartenschlager R, Lohmann V. 2000. Replication of hepatitis C virus. J. Gen. Virol. 81:1631–1648 - PubMed
-
- Boulant S, et al. 2006. Structural determinants that target the hepatitis C virus core protein to lipid droplets. J. Biol. Chem. 281:22236–22247 - PubMed
-
- Boulant S, Targett-Adams P, McLauchlan J. 2007. Disrupting the association of hepatitis C virus core protein with lipid droplets correlates with a loss in production of infectious virus. J. Gen. Virol. 88:2204–2213 - PubMed
-
- Choo QL, et al. 1989. Isolation of a cDNA clone derived from a blood-borne non-A, non-B viral hepatitis genome. Science 244:359–362 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

