Cerebrospinal fluid interleukin-10 is a potentially useful biomarker in immunocompetent primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL)
- PMID: 22156547
- PMCID: PMC3280797
- DOI: 10.1093/neuonc/nor203
Cerebrospinal fluid interleukin-10 is a potentially useful biomarker in immunocompetent primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL)
Abstract
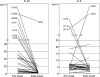
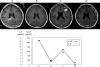
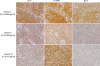
The diagnosis of primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL) by radiographical examination is often difficult because of its similarity to other brain tumors. To test whether interleukin-10 (IL-10) and IL-6 can be used to distinguish PCNSL from other brain tumors that are radiographically similar, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) levels of IL-10 and IL-6 were measured in 66 patients with intracranial tumors (PCNSLs: 26 cases; other brain tumors: 40 cases). In the patients with PCNSLs, the median CSF levels of IL-10 and IL-6 were 27 pg/mL and 5.4 pg/mL, respectively. The CSF IL-10 and IL-6 levels were significantly higher in PCNSLs than in the other brain tumors. To validate the diagnostic value of CSF IL-10 in PCNSL, we prospectively examined 24 patients with brain lesions that were suspected to be PCNSL. We observed that the CSF IL-10 levels were significantly higher in PCNSLs than in other brain tumors. At an IL-10 cutoff level of 9.5 pg/mL, the sensitivity and specificity were 71.0% and 100%, respectively. After therapy, the CSF IL-10 levels were decreased in all patients and were increased at relapse in most of these patients. Immunohistochemically, all PCNSLs, except for 1 unclassified PCNSL, expressed both IL-10 and IL-10 receptor-A. In the patients with high CSF IL-10, IL-10 expression levels in tumor were relatively higher, compared with low CSF IL-10; however, there was no significant difference between these groups. In addition, elevated CSF level of IL-10 was significantly associated with having a shorter progression-free survival (hazard ratio, 3.37; 95% confidence interval, 0.985-11.528; log-rank, P= .038). These results indicate that the CSF level of IL-10 may be a useful diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in patients with PCNSLs.
Figures


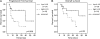
Similar articles
-
The CSF IL-10 concentration is an effective diagnostic marker in immunocompetent primary CNS lymphoma and a potential prognostic biomarker in treatment-responsive patients.Eur J Cancer. 2016 Jul;61:69-76. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2016.03.080. Epub 2016 May 5. Eur J Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27156226
-
Cerebrospinal Fluid IL-10 and IL-10/IL-6 as Accurate Diagnostic Biomarkers for Primary Central Nervous System Large B-cell Lymphoma.Sci Rep. 2016 Dec 7;6:38671. doi: 10.1038/srep38671. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27924864 Free PMC article.
-
Clinicopathological analysis and specific discriminating markers of interleukin detection in cerebrospinal fluid with primary central nervous system lymphoma: results from a retrospective study.Ann Hematol. 2023 Aug;102(8):2153-2163. doi: 10.1007/s00277-023-05301-7. Epub 2023 Jun 8. Ann Hematol. 2023. PMID: 37289220
-
[New developments in diagnosis and therapy of primary non-Hodgkin's lymphoma of the central nervous system].Nervenarzt. 1997 Apr;68(4):298-308. doi: 10.1007/s001150050128. Nervenarzt. 1997. PMID: 9273459 Review. German.
-
Diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of primary central nervous system lymphoma in the elderly population (Review).Int J Oncol. 2021 Mar;58(3):371-387. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2021.5180. Epub 2021 Feb 1. Int J Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33650642 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
STAT3 activation is associated with cerebrospinal fluid interleukin-10 (IL-10) in primary central nervous system diffuse large B cell lymphoma.J Neurooncol. 2015 Sep;124(2):165-74. doi: 10.1007/s11060-015-1843-9. Epub 2015 Jun 17. J Neurooncol. 2015. PMID: 26080800
-
Multi-marker algorithms based on CXCL13, IL-10, sIL-2 receptor, and β2-microglobulin in cerebrospinal fluid to diagnose CNS lymphoma.Cancer Med. 2020 Jun;9(12):4114-4125. doi: 10.1002/cam4.3048. Epub 2020 Apr 20. Cancer Med. 2020. PMID: 32314548 Free PMC article.
-
Role of microRNAs in primary central nervous system lymphomas.Cell Prolif. 2016 Apr;49(2):147-53. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12243. Epub 2016 Mar 16. Cell Prolif. 2016. PMID: 26990358 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Primary central nervous system lymphoma: clinicopathological and genomic insights for therapeutic development.Brain Tumor Pathol. 2021 Jul;38(3):173-182. doi: 10.1007/s10014-021-00408-z. Epub 2021 Jul 13. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2021. PMID: 34255226 Review.
-
CSF interleukin 6 is a useful marker to distinguish pseudotumoral CNS inflammatory diseases from primary CNS lymphoma.J Neurol. 2021 Aug;268(8):2890-2894. doi: 10.1007/s00415-021-10453-5. Epub 2021 Feb 20. J Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33609156
References
-
- Olson JE, Janney CA, Rao RD, et al. The continuing increase in the incidence of primary central nervous system non-Hodgkin lymphoma: a surveillance, epidemiology, and end results analysis. Cancer. 2002;95:1504–1510. doi:10.1002/cncr.10851. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sierra del Rio M, Rousseau A, Soussain C, et al. Primary CNS lymphoma in immunocompetent patients. Oncologist. 2009;14:526–539. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2008-0236. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bataille B, Delwail V, Menet E, et al. Primary intracerebral malignant lymphoma: report of 248 cases. J Neurosurg. 2000;92:261–266. doi:10.3171/jns.2000.92.2.0261. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bernstein M, Berger M. Neuro-Oncology: The Essentials. New York, NY: Thieme Medical Publishers; 2000.
-
- Antinori A, De Rossi G, Ammassari A, et al. Value of combined approach with thallium-201 single-photon emission computed tomography and Epstein-Barr virus DNA polymerase chain reaction in CSF for the diagnosis of AIDS-related primary CNS lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17:554–560. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

