Typhoid fever: "you can't hit what you can't see"
- PMID: 22156762
- PMCID: PMC3370952
- DOI: 10.4161/gmic.18602
Typhoid fever: "you can't hit what you can't see"
Abstract
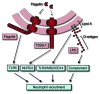
The host restricts dissemination of invasive enteric pathogens, such as non-typhoidal Salmonella serovars, by mounting acute inflammatory responses characterized by the recruitment of neutrophils. However, some enteric pathogens, such as Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi (S. typhi), can bypass these defenses and cause an invasive bloodstream infection known as typhoid fever. Recent studies on virulence mechanisms of S. typhi suggest that tight regulation of virulence gene expression during the transition from the intestinal lumen into the intestinal mucosa enables this pathogen to evade detection by the innate immune system, thereby penetrating defenses that prevent bacterial dissemination. This example illustrates how the outcome of host pathogen interaction at the intestinal mucosal interface can alter the clinical presentation and dictate the disease outcome.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Loss of very-long O-antigen chains optimizes capsule-mediated immune evasion by Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi.mBio. 2013 Jul 16;4(4):e00232-13. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00232-13. mBio. 2013. PMID: 23860765 Free PMC article.
-
The sulfur assimilation pathway mitigates redox stress from acidic pH in Salmonella Typhi H58.mBio. 2025 Jul 9;16(7):e0046725. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00467-25. Epub 2025 May 27. mBio. 2025. PMID: 40422406 Free PMC article.
-
Propionylation of Fis K32 in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi: a key modification affecting pathogenicity.Future Microbiol. 2025 Mar;20(4):295-303. doi: 10.1080/17460913.2025.2460338. Epub 2025 Jan 30. Future Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39885648
-
Clinical pathogenesis of typhoid fever.J Infect Dev Ctries. 2008 Aug 30;2(4):260-6. doi: 10.3855/jidc.219. J Infect Dev Ctries. 2008. PMID: 19741286 Review.
-
Now you see me, now you don't: the interaction of Salmonella with innate immune receptors.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2015 Apr;13(4):206-16. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro3428. Epub 2015 Mar 9. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25749454 Review.
Cited by
-
Differential susceptibility and maturation of thymocyte subsets during Salmonella Typhimurium infection: insights on the roles of glucocorticoids and Interferon-gamma.Sci Rep. 2017 Jan 16;7:40793. doi: 10.1038/srep40793. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28091621 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of very-long O-antigen chains optimizes capsule-mediated immune evasion by Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi.mBio. 2013 Jul 16;4(4):e00232-13. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00232-13. mBio. 2013. PMID: 23860765 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms to Evade the Phagocyte Respiratory Burst Arose by Convergent Evolution in Typhoidal Salmonella Serovars.Cell Rep. 2018 Feb 13;22(7):1787-1797. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.01.016. Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 29444431 Free PMC article.
-
A Naturally Occurring Deletion in FliE from Salmonella enterica Serovar Dublin Results in an Aflagellate Phenotype and Defective Proinflammatory Properties.Infect Immun. 2017 Dec 19;86(1):e00517-17. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00517-17. Print 2018 Jan. Infect Immun. 2017. PMID: 29061704 Free PMC article.
-
Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi impairs CD4 T cell responses by reducing antigen availability.Infect Immun. 2014 Jun;82(6):2247-54. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00020-14. Epub 2014 Mar 18. Infect Immun. 2014. PMID: 24643532 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Janeway CA., Jr. Approaching the asymptote? Evolution and revolution in immunology. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1989;54:1–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
